 |
 |
AbstractMucormycosis is one of the most fatal and rapidly progressive fungal infections in humans; among its many forms. rhinocerebral mucormycosis is the most common. It is known to occur as opportunistic infection in patients with uncontrolled diabetes, metabolic disorders, organ transplantation, or autoimmune disease with prolonged steroid use. PottŌĆÖs puffy tumor is the subperiosteal abscess of the frontal bone caused by trauma complication or frontal sinusitis. It is considered as a very rare complication since the dawn of antibiotic treatments. We report a case of chronic rhinocerebral mucormycosis involving PottŌĆÖs puffy tumor in a patient receiving immunosuppressive therapy after lung transplantation.
ņä£ ļĪĀļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”Ø(mucormycosis)ņØĆ ņØĖĻ░äņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ņ¦äĻĘĀ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ ņżæ Ļ░Ćņן ņ╣śļ¬ģņĀüņØ┤ļ®░ ļ╣ĀļźĖ ņåŹļÅäļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļŖö ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ╣äļćīļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”Ø(rhinocerebral mucormycosis)ņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן ĒØöĒĢ£ ĒśĢĒā£ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż[1,2]. ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļŗ╣ļć©, ļīĆņé¼ņןņĢĀ, ņןĻĖ░ņØ┤ņŗØ ĒÖśņ×É, ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ļź╝ ņןĻĖ░Ļ░ä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņ×ÉĻ░Ćļ®┤ņŚŁņ¦łĒÖś ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ ĻĖ░ĒÜīĻ░ÉņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®░ ĻĄŁļé┤ņŚÉļŖö 1980ļģäļīĆ ņØ┤Ēøä ņ×ÉĻ░Ćļ®┤ņŚŁņ¦łĒÖś ļ░Å ņןĻĖ░ņØ┤ņŗØ ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļŖśņ¢┤ļéśĻ▓ī ļÉśļ®┤ņä£ ņןĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļ®┤ņŚŁņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ ļ░Å ņŖżĒģīļĪ£ņØ┤ļō£ ņé¼ņÜ® ņ”ØĻ░ĆļĪ£ ļ░£ņāØļźĀņØ┤ ņĀÉņ░© ļŖśņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ņČöņäĖņØ┤ļŗż[3-5].
PottŌĆÖs puffy tumor(PPT)ļŖö ņÖĖņāüņØ┤ļéś ņĀäļæÉļÅÖ ļČĆļ╣äļÅÖņŚ╝ņØś ĒĢ®ļ│æņ”Øņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ņĀäļæÉĻ│©ņØś Ļ│©ļ¦ēĒĢś ļåŹņ¢æņØ┤ļ®░ ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ņØś ļ│┤ĻĖēĒÖö ņØ┤Ēøä ļ¦żņÜ░ ļō£ļ¼╝Ļ▓ī ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļ®░ ņä▒ņØĖņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ļŖö ļŹö ĒؼĻĘĆĒĢ£ ņ¦łļ│æņØ┤ļŗż. ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĒÅÉņØ┤ņŗØņØä ļ░øņØĆ Ēøä ļ®┤ņŚŁņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ļź╝ ļ│ĄņÜ® ņżæņØĖ ņä▒ņØĖ ĒÖśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ļ¦īņä▒ņĀüņØĖ ĒśĢĒā£ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļ®░ PPTļź╝ ļÅÖļ░śĒĢ£ ļ╣äļćīļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”Ø 1ņśłļź╝ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśņśĆĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļ¼ĖĒŚī Ļ│Āņ░░Ļ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒĢśļŖö ļ░öņØ┤ļŗż(Fig. 1).
ņ”Ø ļĪĆ55ņäĖ ņŚ¼ņ×É ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć 6Ļ░£ņøö ņĀäļČĆĒä░ ņ¦ĆņåŹļÉśļŖö ņóīņĖĪ ņĢłņÖĆ ņŻ╝ņ£ä ļČĆņóģĻ│╝ ļÅÖĒåĄņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłĻ│╝ ņ¦äļŻī ņżæ, 4Ļ░£ņøö ņĀäļČĆĒä░ ņ▓£ņ▓£Ē׳ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļŖö ņóīņĖĪ ņØ┤ļ¦ł 2 cm Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņØś ļÅīņČ£ļÉ£ ĒśĢĒā£ņØś ļ░£ņĀüĻ│╝ ņĢĢĒåĄņØ┤ ļÅÖļ░śļÉ£ ņóģņ░Įņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│ĖĻ│╝ ņÖĖļל ļé┤ņøÉĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 2A). ĒÖśņ×ÉļŖö Ļ│ĀĒśłņĢĢ, ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļŗ╣ļć©, ļ¦īņä▒ņŗĀļČĆņĀäņØś Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ļĀźņØ┤ ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, 10Ļ░£ņøö ņĀä ĒÅÉ ņØ┤ņŗØ Ēøä ļ®┤ņŚŁņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ļź╝ ļ│ĄņÜ® ņżæņØĖ ņāüĒā£ņśĆļŗż.
Lipoid pneumoniaņØś ĻĖēņä▒ ņĢģĒÖöļĪ£ ņØæĻĖēņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÅÉ ņØ┤ņŗØņØä ļ░øņØĆ ĒÖśņ×ÉņśĆĻĖ░ņŚÉ ĒÅÉ ņØ┤ņŗØ ņĀä paranasal sinus viewļŖö ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ņĢłņÖĆ ņŻ╝ņ£ä ļČĆņóģņØä ņØ┤ņ£ĀļĪ£ ĒÅÉ ņØ┤ņŗØ 4, 6, 10Ļ░£ņøö Ēøä ņĢłĻ│╝ņŚÉņä£ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£ caldwell viewņāü ņóīņĖĪ ņĀäļæÉļÅÖņØś Ļ░ĆņĖĪ Ļ▓ĮĻ│ä Ļ▓ĮĒÖö ļ░Å Ļ│©ĒīīĻ┤┤ņä▒ ļ│ĆĒÖöļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļ®░ ņĀäļæÉļÅÖņØ┤ ĒÖĢņןļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ļ╣äļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮĻ▓Ćņé¼ņāü ļ╣äĻ░Ģ ļé┤ Ļ░ĆĒö╝ņÖĆ ņÜ®ņóģņä▒ ņĪ░ņ¦üņØ┤ ņżæļ╣äĻ░æĻ░£ ņŻ╝ņ£äņŚÉņä£ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłļŗż. Orbit computed tomography(CT)ņāü ņØ┤ļ¦łņØś ņóģņ░ĮĻ│╝ ņØ┤ņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņĀäļæÉļÅÖ ļé┤ ļ│æļ│Ć ļ░Å ņāüņĢłņÖĆļ▓ĮņØś Ļ▓░ņåÉņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 2B and C).
ņóīņĖĪ ņØ┤ļ¦ł ņóģņ░ĮņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ external eyebrow incision ņĀæĻĘ╝ļ▓ĢņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢ£ ļ░░ļåŹ ļ░Å ņĪ░ņ¦üĻ▓Ćņé¼ļź╝ ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ│æļ”¼ ņåīĻ▓¼ņāü Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņĪ░ņ¦üļ¦ī Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ņ¦äĻĘĀņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ļ░░ņ¢æĻ▓Ćņé¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ extended spectrum ╬▓-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniaeĻ░Ć ļÅÖņĀĢļÉśņ¢┤ 8ņŻ╝Ļ░äņØś IV ertapenem sodium(1 g/day) ņ╣śļŻī Ēøä ĒÖśņ×É ņ”ØņāüņØ┤ ņØ╝ļČĆ ĒśĖņĀäļÉśņŚłļŗż.
ņĀłĻ░£ ļ░Å ļ░░ļåŹ ņŗ£Ē¢ē 3Ļ░£ņøö Ēøä, ņÖĖļל ļ╣äļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņåīĻ▓¼ņāü ņżæļ╣äĻ░æĻ░£ļĪ£ ņČöņĀĢļÉśļŖö Ļ│© ņĀłĒÄĖņØ┤ ļ╣äĻ░Ģ ļé┤ņŚÉ ļģĖņČ£ļÉśņ¢┤ ņĪ░ņ¦üĻ▓Ćņé¼ļź╝ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ļŗżņłśņØś ņ╣©ņŖĄņĀü ņ¢æņāüņØś ĻĘĀņé¼ ņåīĻ▓¼ņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”Ø ļśÉļŖö ņ╣©ņŖĄņĀü ņĢäņŖżĒÄśļź┤ĻĖĖļŻ©ņŖżņ”Ø(aspergillosis)ņØ┤ ņØśņŗ¼ļÉśņŚłļŗż. CTņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļæÉ-ņĢłļ®┤ļČĆņØś ņŚ░ņĪ░ņ¦ü ļČĆņóģ, ņĀäļæÉļÅÖ Ļ│©ĒīīĻ┤┤ņÖĆ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļé┤ļČĆ ļé┤ņÜ®ļ¼╝ņØś ņäØĒÜīĒÖö ņåīĻ▓¼ņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ MRI T1 Ļ░ĢņĪ░ņśüņāüņŚÉņä£ ņĀĆņŗĀĒśĖ Ļ░ĢļÅä, T2ņŚÉņä£ ļČłĻĘĀņ¦łĒĢ£ Ļ░ĢļÅäņØś fungal ballļĪ£ ņØśņŗ¼ļÉśļŖö ļé┤ņÜ®ļ¼╝ņØ┤ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ļīĆļćī ņ╣©ņŖĄņØĆ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņ£╝ļéś ņŻ╝ļ│ĆļČĆļĪ£ Ļ│Āļ░ĆļÅä ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ņåīĻ▓¼ņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłļŗż. ĒĢ┤ļ®┤ņĀĢļ¦źļÅÖ ļ░Å ļé┤Ļ▓ĮļÅÖļ¦ź ĒśłņĀäņ”ØņØĆ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż (Fig. 3).
ņ╣©ņŖĄņä▒ ņ¦äĻĘĀņä▒ ļČĆļ╣äļÅÖņŚ╝ ņ¦äļŗ©ĒĢśņŚÉ ņłśņłĀņØä Ļ│äĒÜŹĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļéś ĻĖ░ņĀĆņ¦łĒÖśņØ┤ ļ¦ÄĻ│Ā ļ¦īņä▒ņĀüņØĖ ņ¢æņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖśņ×É ļ░Å ļ│┤ĒśĖņ×ÉĻ░Ć Ļ▒░ļČĆĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ņŚÉ liposomal formņØś IV amphotericin B(250 mg/day) ņ╣śļŻī ņŗ£Ē¢ē ņżæ 3ņŻ╝ņ¦Ė ņ”Øņāü ņĢģĒÖö ļ░Å headacheļź╝ ĒśĖņåīĒĢśņŚ¼ ļŗżņŗ£ ņäżļōØ Ēøä ņłśņłĀņØä Ļ│äĒÜŹĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņłśņłĀ ņŗ£ ļæÉĻ░£ņĀĆ Ļ▓░ņåÉ, ļćīņ▓ÖņłśņĢĪ ņ£ĀņČ£ņØä ņÜ░ļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņÜ░ņäĀ ļæÉĻ░£ņĢłļ®┤ņĀłņĀ£ņłĀņØä ĒåĄĒĢ£ Ļ┤æļ▓öņ£ä ņĀ£Ļ▒░ļź╝ Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś ņĀäņŗĀ ņāüĒā£ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ĒÜīļ│ĄņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜĖ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļäżļ╣äĻ▓īņØ┤ņģś ļ│┤ņĪ░ĒĢś draf IIb ņłĀĻĖ░ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ļ╣äņĀäļæÉĻ┤ĆņØä Ļ░£ļ░®ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśļŖö Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņĪ░ņ¦üņØä microdebriderņÖĆ ļō£ļ”┤ņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¬©ļæÉ ņĀ£Ļ▒░ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░ ļ│æļ”¼ņĪ░ņ¦üĻ▓Ćņé¼ņāü ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”Øņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦äļŗ©ļÉśņŚłļŗż(Fig. 4).
ĒÖśņ×ÉļŖö ņłśņłĀ Ēøä ļ®┤ņŚŁņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ ņĪ░ņĀłņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ ĒśĖĒØĪĻĖ░ ļé┤Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ņĀäĻ│╝ Ēøä liposomal formņØś IV amphotericin B(250 mg/day)ļź╝ ņłśņłĀ Ēøä 5ņŻ╝Ļ░ä Ēł¼ņŚ¼ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░ Ēć┤ņøÉ Ēøä Ļ▓ĮĻĄ¼ ĒĢŁņ¦äĻĘĀņĀ£ļ¦ī(posaconazole 300 mg/day) 10ņØ╝Ļ░ä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņłśņłĀ Ēøä ĒĢ£ ļŗ¼ņ¦Ė ņŗ£Ē¢ēĒĢ£ CT ļ░Å ļ╣äļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮĻ▓Ćņé¼ņāü ņŻ╝ņ£ä ņĀÉļ¦ēņĪ░ņ¦üņØ┤ ĒÜīļ│ĄļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 5A). ņłśņłĀ 1ļģä ĒøäļČĆĒä░ ļ╣äņ╣©ņŖĄņĀü ĒśĢĒā£ņØś Ļ│░ĒīĪņØ┤ ļŹ®ņ¢┤ļ”¼Ļ░Ć Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļéś ļō£ļĀłņŗ▒ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņēĮĻ▓ī ņĀ£Ļ▒░ļÉśņŚłļŗż(Fig. 5B). Ēśäņ×¼ ņłśņłĀ Ēøä 18Ļ░£ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņ╣©ņŖĄņĀüņØĖ Ļ│░ĒīĪņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņ”ØņØĆ ļŹö ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ņāüĒā£ļĪ£ Ļ▓ĮĻ│╝ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ ņżæņØ┤ļŗż(Fig. 5C and D).
Ļ│Ā ņ░░ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØĆ ņŗØĻĘĀņ×æņÜ®ņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ ļ®┤ņŚŁņĀĆĒĢś ņāüĒā£ļéś ļŗ╣ļć© ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö ĻĖ░ĒÜīĻ░ÉņŚ╝ņØ┤ļŗż. ĻĖēņä▒ĒśĢņØĆ ļ®┤ņŚŁņĀĆĒĢś ņāüĒā£ņØś ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéś 10ņØ╝ ņØ┤ļé┤ņØś ļ╣ĀļźĖ ņĀäĻ░£ ļ░Å ļåÆņØĆ ņé¼ļ¦ØļźĀņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļ®░ ļ¦īņä▒ĒśĢņØĆ ļé«ņØĆ ļĀłļ▓©ņØś ļ®┤ņŚŁņĀĆĒĢś ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ĒśĖļ░£ĒĢśļ®░ Ļ│ĀņĀäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö 4ņŻ╝ ņØ┤ņāü, ņØ╝ļČĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö 7Ļ░£ņøö ņØ┤ņāü ņ¦ĆņåŹļÉśļŖö Ļ▓Įņ”ØĻ│╝ ļ¼┤ĒåĄņä▒ Ēś╣ņØĆ ņ£ĪņĢäņóģņä▒ ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņØ┤ļŻ©Ļ│Ā ņäØĒÜīĒÖöļź╝ ĒŖ╣ņ¦Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ£ļŗż[6]. ļśÉĒĢ£ ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØĆ ļ░£ņāØ ņןņåīņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ļÅä ļ│Ė ņ”ØļĪĆņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļŹö ņ╣śļ¬ģņĀüņØĖ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ╣ä-ņĢłņÖĆļīĆļćīĒśĢ Ēś╣ņØĆ ļ╣äļćīĒśĢ(rhino-orbito-cerebral)Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉņĀü ņóŗņØĆ ņśłĒøäļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö ļ╣äļČĆļ╣äļÅÖĒśĢ(sinonasal)ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśļłī ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[7]. ļ¦īņä▒ ļ╣äļćīļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØĆ 1960ļģäļīĆ ņØ┤ĒøäļĪ£ PubMedņŚÉ ņĢĮ 22ņśłļ¦īņØ┤ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ĒؼĻĘĆĒĢ£ ņ¦łĒÖśņØ┤ļ®░ ĻĄŁļé┤ņŚÉņä£ļÅä 2016ļģäņŚÉ ĒĢ£ ņ”ØļĪĆĻ░Ć ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉ£ ļ░ö ņ׳ņ£╝ļéś ļ│Ė ņ”ØļĪĆņÖĆļŖö ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ņןĻĖ░ ņØ┤ņŗØ ļ░Å ļ®┤ņŚŁ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ ļ│ĄņÜ®ļĀźņØ┤ ņŚåņŚłņ£╝ļ®░ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņĀü ņłśņłĀņØ┤ ņĢäļŗī Ļ┤æļ▓öņ£ä ņłśņłĀņĀü ņĀłņĀ£ļź╝ ĒĢśņśĆļŗż[6,8].
ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØĆ ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļŗ╣ļć©ņÖĆ ņ╝ĆĒåĀņé░Ēśłņ”ØņØś ņ£Āļ¼┤Ļ░Ć ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ļŹ░ ņØ┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ņżæņä▒ĻĄ¼ Ļ░Éņåī ļ░Å ĒÖöĒĢÖņŻ╝ņä▒(chemotaxis)ņØś ņĀĆĒĢ┤Ļ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļéś ņŗØĻĘĀņ×æņÜ®ņØä ņĢĮĒÖöņŗ£Ēéżļ®░ ļŹö ļéśņĢäĻ░Ć ņ╝ĆĒåĀņé░Ēśłņ”ØņØĆ Ēśłņ▓Ł ņ▓ĀņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£ņ╝£ ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØś ņ¦äĒ¢ēņØä Ļ░ĆņåŹĒÖöņŗ£ĒéżĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż[9]. ļ│Ė ņ”ØļĪĆņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļŗ╣ļć©ņØś Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ļĀźņØĆ ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļéś ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢ£ ņ╝ĆĒåĀņé░Ēśłņ”ØņØĆ ņŚåņŚłļŗż.
ņ×äņāü ņ¢æņāüņØĆ ļīĆĻ░£ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖ ļČĆļ╣äļÅÖņŚ╝ ņ”Øņāü ļ░Å ņĢłļ®┤ĒåĄ, ņĢłņÖĆļČĆņóģ, ļ░£ņŚ┤, Ēśłņä▒ ļ╣äļŻ© ļō▒ņØ┤ ļ©╝ņĀĆ ļéśĒāĆļéśļ®░, ņ▓½ ņ”Øņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłĻ│╝ņĀü ņ”ØņāüņØä ĒśĖņåīĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦Äļŗż[10]. ļ│æņØ┤ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉ©ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņĢłĻĘ╝ļ¦łļ╣ä, ņĢłĻ▓ĆĒĢśņłś, ņĢłļ®┤ņŗĀĻ▓Įļ¦łļ╣ä ļō▒ņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ļ¦īņä▒ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒĢ┤ļ®┤ņĀĢļ¦źļÅÖ ļ░Å ļé┤Ļ▓ĮļÅÖļ¦ź ĒśłņĀäņ”ØņØ┤ ļŹö ņל ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé£ļŗż[11]. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ļ╣äļćīļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØ┤ ņĀäļæÉĻ│©ņØś Ļ│©ļ¦ēĒĢś ļåŹņ¢æņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö ļ¦żņÜ░ ļō£ļ¼╝ļ®░ ĻĄŁļé┤ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ”ØļĪĆņŚÉ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ĒĢ£ļŗż[12].
ļ¦īņä▒ ļ╣äļćīļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņØś ņøÉņØĖ ĻĘĀņØĆ ņ”ØļĪĆĻ░Ć ņĀüņ¢┤ Mucor ramosissimus, Rhizopus nigricans, Mucor irregularis ņĀĢļÅäļ¦īņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļ¬©ļæÉ ņĢĮ 36┬░C ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņ▓┤ņś©Ļ│╝ ņ£Āņé¼ĒĢ£ ņś©ļÅäņŚÉņä£ ņä▒ņןņØ┤ ļæöĒÖöļÉśĻ▒░ļéś ļ®łņČöļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ ņØ┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ļ╣äĻĄÉņĀü ļŖÉļ”░ ņ¦äĒ¢ē ņ¢æņāüņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņČöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[10,13].
ņØ┤ĒĢÖņĀü Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņāüņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ╣äĻ░Ģ ļ░Å ļČĆļ╣äļÅÖņØś Ļ▓ĆņØĆņāē Ļ░ĆĒö╝, Ļ┤┤ņé¼ņä▒ ņĪ░ņ¦ü ņåīĻ▓¼ ļō▒ņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉ£ļŗż[14]. CT ņåīĻ▓¼ņāü Ļ│©ļ»Ėļ×ĆĻ│╝ Ļ│©ĒīīĻ┤┤ ļ░Å ņäØĒÜīĒÖö ņåīĻ▓¼ņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, MRI T1, T2 Ļ░ĢņĪ░ņśüņāü ļ¬©ļæÉņŚÉņä£ ņĀĆņŗĀĒśĖ Ļ░ĢļÅäņØś ļ│æļ│ĆņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ļ¦Äļŗż. ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ ļ╣äĒŖ╣ņØ┤ņĀüņØĖ ņśüņāü ņåīĻ▓¼ļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦īņä▒ ņ╣©ņŖĄņĀü ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØĻ│╝ ņĢģņä▒ ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒ׳ Ļ░Éļ│äĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ░ļ»ĆļĪ£ ļ│æļ”¼ ņ¦äļŗ©ņØ┤ ĒÖĢņ¦äņŚÉ ĒĢäņłśņĀüņØ┤ļ®░ GrocottŌĆÖs methenamine silver-periodic acid Schiff, hematoxylin and eosin ņŚ╝ņāēņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ¦üĻ░üņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ćļź╝ ļé┤ļŖö Ļ▓®ļ▓Į ņŚåļŖö ĻĘĀņé¼ļź╝ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[3].
PPTļŖö ņĀäļæÉĻ│©ņØś Ļ│©ļ¦ēĒĢśļåŹņ¢æņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢśļ®░ ņĀäļæÉļÅÖņØś ņŚ╝ņ”ØņØ┤ ļłäĻ│ĄņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ĒīīĻĖēļÉśņ¢┤ Ļ│©ņłśņŚ╝ ļ░Å ļåŹņ¢æņØś ĒśĢņä▒ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗż. 1768ļģä Percivall PottņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņÖĖņāüņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ▓śņØī ņĀĢņØśļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļéś ņØ┤Ēøä ņĀäļæÉļÅÖ ļČĆļ╣äļÅÖņŚ╝ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ņ”ØļĪĆļōżļÅä ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņÖäņĀäĒ׳ ļ░£ļŗ¼ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņĀäļæÉļÅÖņØś ĒĢ┤ļČĆĒĢÖņĀü ĻĄ¼ņĪ░ļéś ņĢäņØ┤ļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ĒØöĒĢ£ ĒīÉņé¼ņØ┤ņĀĢļ¦źņØś Ēśłļźś ņ”ØĻ░ĆļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ĒØöĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ░£ļ│æĒĢśņŚ¼ ņä▒ņØĖņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ļŖö ļō£ļ¼╝ļ®░ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ 10~20ņäĖņŚÉ ĒØöĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ░£ļ│æĒĢ£ļŗż. ņĀäļæÉĻ│© ĒåĄņ”Ø, ļæÉĒåĄ, ņĢłņÖĆ ļČĆņóģ, ļ░£ņŚ┤ ļō▒ņØś ņ×äņāü ņ”ØņāüņØ┤ ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ Ļ░ÉņŚ╝ņØ┤ ļīĆļćīĻ╣īņ¦Ć ĒīīĻĖēļÉĀ ņŗ£ ļćīņłśļ¦ēņŚ╝, Ļ▓Įļ¦ēņÖĖ ļåŹņ¢æ, ļćīļåŹņ¢æņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢģĒÖöļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ ņ╣śļŻīļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ļ│┤ĒåĄ ļČĆņĀüĒĢ®ĒĢśļ®░ ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņłśņłĀņĀü ļ░░ļåŹņØä Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöļĪ£ ĒĢ£ļŗż[15]. ļ│Ė ņ”ØļĪĆļŖö ļ¬©ĻĘĀņ”ØņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ PPTņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļĪ£ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢ£ Ļ┤┤ņé¼ ņĪ░ņ¦üņØś ņĀłņĀ£, amphotericin BņØś Ēł¼ņŚ¼, ĻĖ░ņĀĆņ¦łĒÖśņØś ĻĄÉņĀĢ ļ░Å ņ╣śļŻīļź╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņŗżņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż[4,14].
ļ│Ė ņ”ØļĪĆņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņØ┤ļ¦łņŚÉ ļÅīņČ£ļÉ£ ĒśĢĒā£ņØś ļ░£ņĀüĻ│╝ ņĢĢĒåĄņØ┤ ļÅÖļ░śļÉ£ ņóģņ░ĮĻ│╝ ņĢłņÖĆļČĆņóģņØä ņ▓½ ņ”Øņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļé┤ņøÉĒĢ£ ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ĒÅÉņØ┤ņŗØ Ēøä ļ®┤ņŚŁņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ ļ│ĄņÜ® ļ░Å ņĪ░ņĀłļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļŗ╣ļć© ļ│æļĀźņØ┤ ļÅÖļ░śļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, PPTĻ░Ć ļÅÖļ░śļÉśņŚłļŗżļŖö ņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś ņ”ØļĪĆļōżĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉ ņŗ£ ņØśļ»ĖĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņ╣śļŻī ļ░®ļ▓ĢļÅä ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖ ļæÉĻ░£ņĢłļ®┤ņĀłņĀ£ņłĀņØ┤ ņĢäļŗī ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ļīĆļæÉļÉśļŖö ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢ£ draf IIb ļ░®ļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ĒĢŁņ¦äĻĘĀņĀ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ņØä ļ│æņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
NotesAuthor Contribution Conceptualization: Hyung-Ju Cho, Jong-Gyun Ha. Data curation: Chan Lee, Sung-Eun Choi, Jong-Gyun Ha. Formal analysis: JongGyun Ha. Investigation: Chan Lee, Sung-Eun Choi. Methodology: Jong-Gyun Ha. Project administration: Hyung-Ju Cho, Jong-Gyun Ha. Resources: Hyung-Ju Cho. Supervision: Hyung-Ju Cho, JongGyun Ha. Validation: Hyung-Ju Cho, Jong-Gyun Ha. Visualization: Chan Lee, Sung-Eun Choi. WritingŌĆöoriginal draft: Chan Lee. WritingŌĆöreview & editing: Jong-Gyun Ha. Fig.┬Ā1.Course of disease and treatment in chronological order. ESBLs-KPN: extended spectrum ╬▓-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Bx: biopsy, Cx: culture, P.O.: peroral. 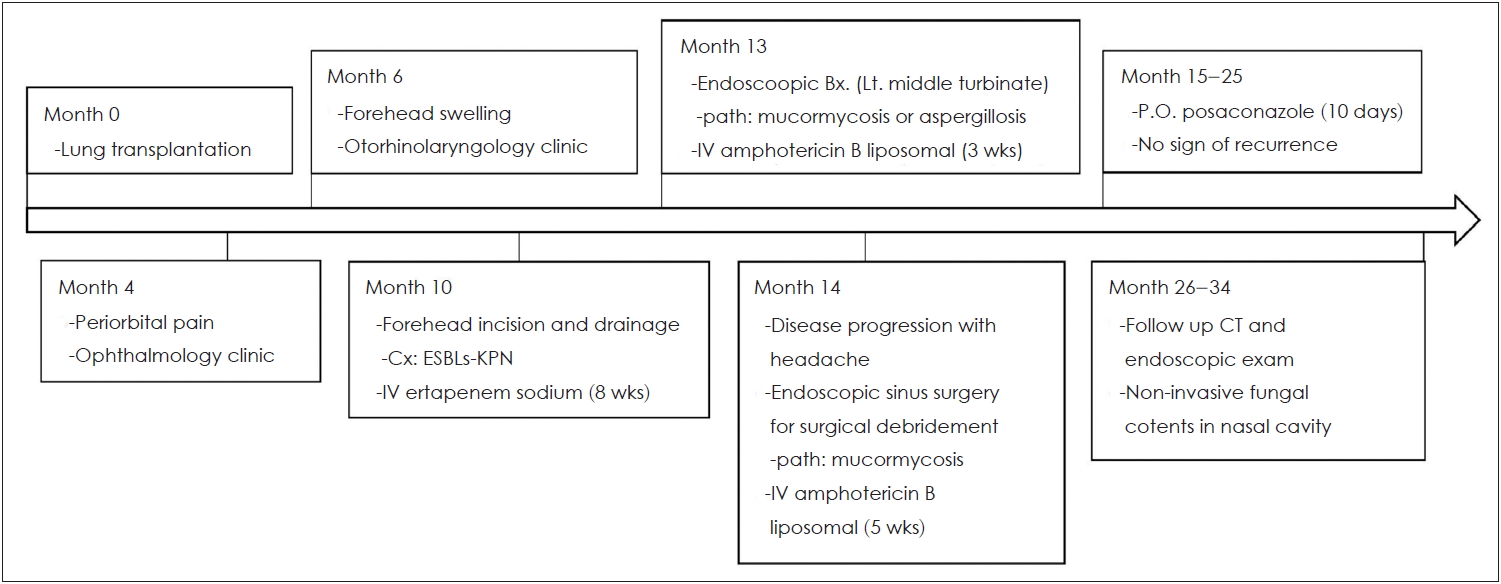
Fig.┬Ā2.Physical appearance and computed tomography (CT) of forehead and frontal sinus lesion. Facial photograph demonstrates swelling of left forehead and periorbital area (A). Orbit CT taken 6 months after lung transplantation shows frontal sinus lesion connected to external forehead swelling in axial (B), sagittal view (C). 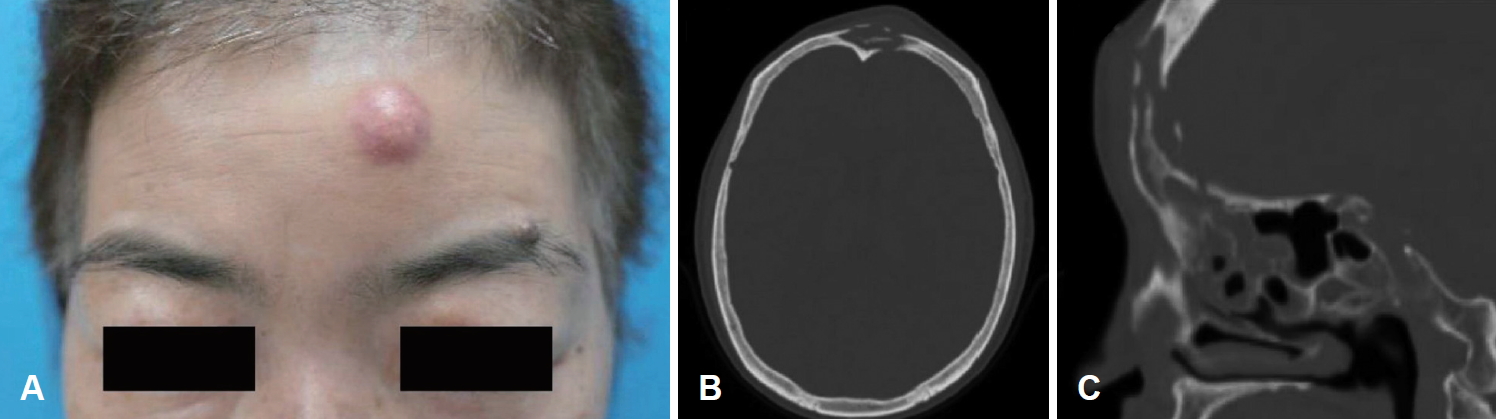
Fig.┬Ā3.Preoperative non-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan and MRI of the frontal sinus lesion taken 13 months after lung transplantation. Axial (A) and coronal view (B) of CT scan show dense opacification and calcification with destruction of posterior wall of left frontal sinus. MRI shows low signal intensity on T1 weighted image (C) and heterogeneous signal intensity on T2 weighted image (D). 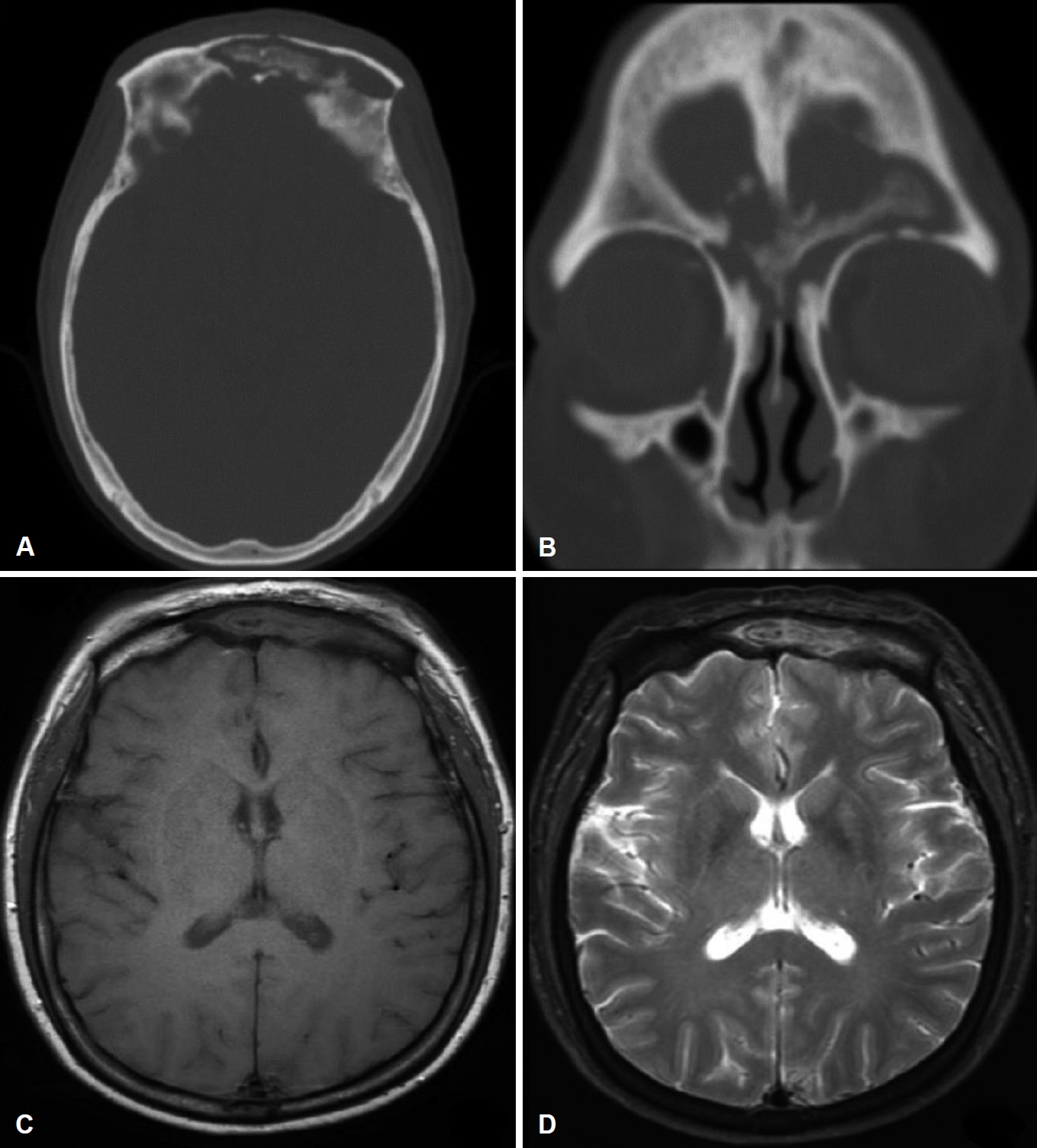
Fig.┬Ā4.Pathological specimen from left frontal sinus lesion shows invasive fungal hyphae without branch and septum, morphologically consistent with mucormycosis. Hematoxylin and eosin stain (A and B). Periodic acid-Schiff diastase stain (C and D). 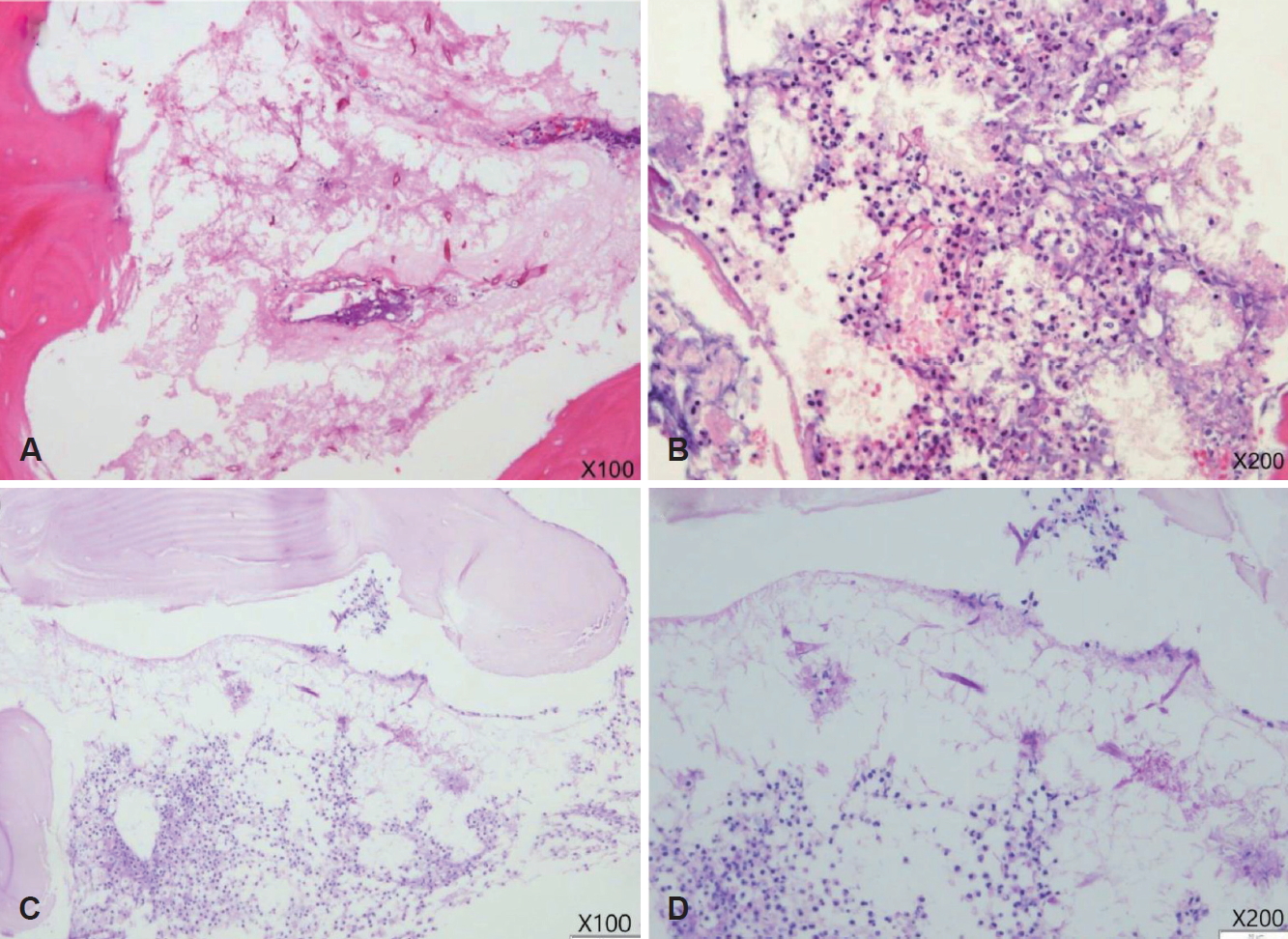
Fig.┬Ā5.Postoperative findings. Nasal endoscopic view (A) 1 month and (B) 18 months after the surgery. Morphologically non-invasive fungal content was noted 1 year after the surgery. However, there was no evidence of invasive fungal infection progression throughout postoperative computed tomography scans with the latest exam 18 months after the surgery (C and D). S, FR, MTr, and MS are labeled in endoscopic findings. S: septum, FR: frontal recess, MTr: middle turbinate remnant, MS: maxillary sinus. 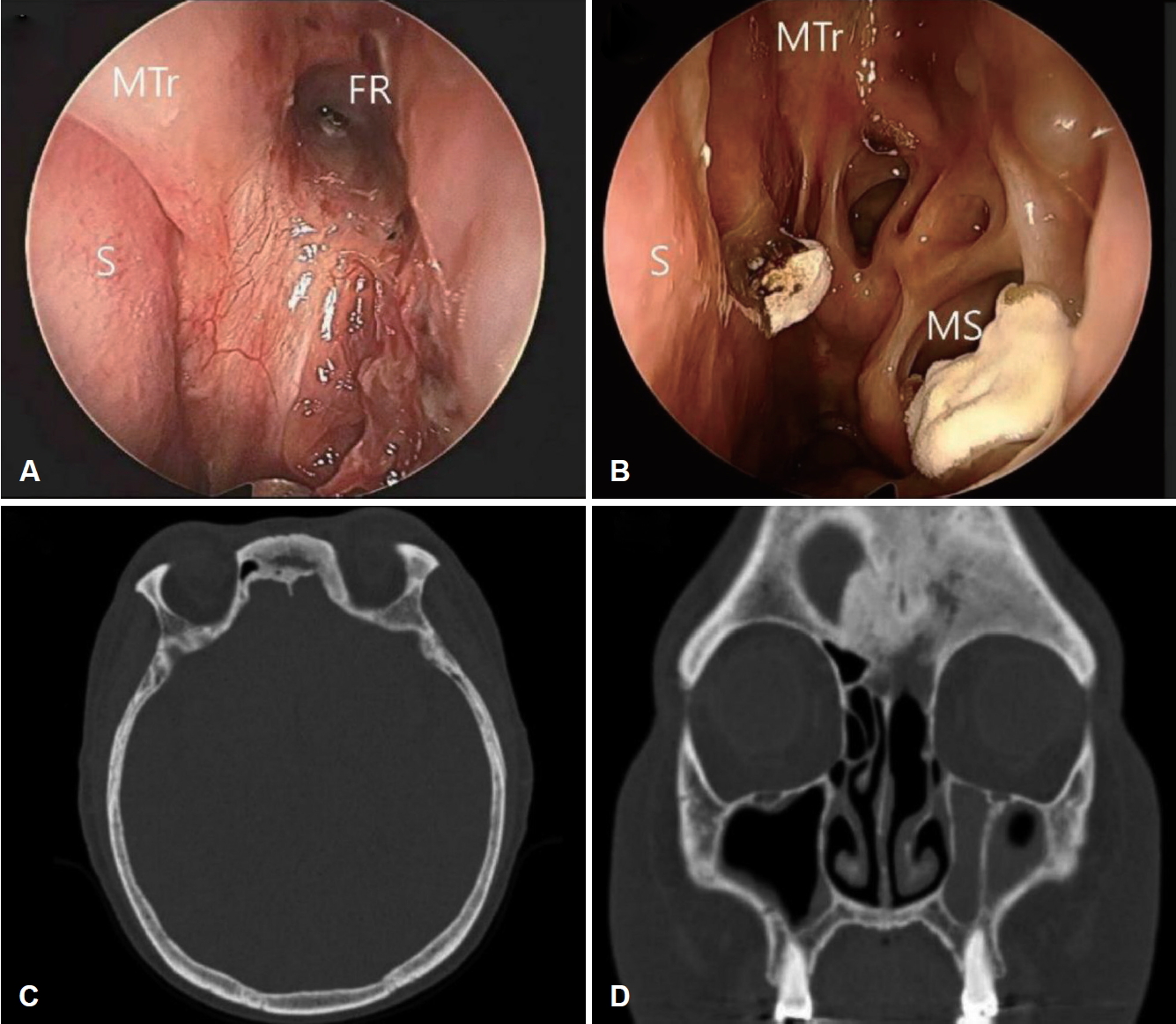
REFERENCES1. Leitner C, Hoffmann J, Zerfowski M, Reinert S. Mucormycosis: Necrotizing soft tissue lesion of the face. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2003;61(11):1354-8.
2. Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, Knudsen TA, Sarkisova TA, Schaufele RL, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: A review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis 2005;41(5):634-53.
3. Jin YW, Kim KH, Cho JS, Cha CI. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis with selective cranial nerve palsy. Korean J OtorhinolaryngolHead Neck Surg 2001;44(6):674-7.
4. Do NY, Lee JH, Dong GW. Clinical study of rhinocerebral mucormycosis. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 2005;48(10):1228-34.
5. Lee SB, Yi JS, Kim JY, Chang C. Rhino-orbito-cerebral mucormycosis complicated as facial paralysis and ophthalmoplegia without rhinologic manifestation. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 2015;58(7):503-8.
6. Guti├®rrez-Delgado EM, Trevi├▒o-Gonz├Īlez JL, Montemayor-Alatorre A, Cece├▒as-Falc├│n LA, Ruiz-Holgu├Łn E, Andrade-V├Īzquez CJ, et al. Chronic rhino-orbito-cerebral mucormycosis: A case report and review of the literature. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2016;6:87-91.
7. Peterson KL, Wang M, Canalis RF, Abemayor E. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis: Evolution of the disease and treatment options. Laryngoscope 1997;107(7):855-62.
8. Kim D, Kim J-w, Ahn S-J, Hong S-L. Chronic invasive sinonasal mucormycosis; A rare disease entity. J Rhinol 2016;23(2):119-23.
9. Spellberg B, Edwards J Jr, Ibrahim A. Novel perspectives on mucormycosis: Pathophysiology, presentation, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005;18(3):556-69.
10. Dimaka K, Mallis A, Naxakis SS, Marangos M, Papadas TA, Stathas T, et al. Chronic rhinocerebral mucormycosis: A rare case report and review of the literature. Mycoses 2014;57(11):699-702.
11. Galetta SL, Wulc AE, Goldberg HI, Nichols CW, Glaser JS. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis: Management and survival after carotid occlusion. Ann Neurol 1990;28(1):103-7.
12. Yoon H, Jeon S-B, Kim HA, Kwon BS, Kim S-H, Kang JK. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis manifested as PottŌĆÖs puffy tumor. J Neurocrit Care 2014;7(2):111-5.
13. Hemashettar BM, Patil RN, OŌĆÖDonnell K, Chaturvedi V, Ren P, Padhye AA. Chronic rhinofacial mucormycosis caused by Mucor irregularis (rhizomucor variabilis) in India. J Clin Microbiol 2011;49(6):2372-5.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 |
 |