트림을 못해 내원한 환자들의 진단과 보툴리늄 독소를 이용한 치료 2예
Two Cases of Diagnosis and Botulinum Toxin Treatment in Patients Who Were Unable to Burp
Article information
Trans Abstract
Retrograde cricopharyngeus dysfunction (R-CPD) is a new syndrome first described in 2019 by Bastian. It is characterized by an inability to belch, along with associated symptoms such as loud gurgling noises, chest and abdominal pain/distention, and excessive flatulence. The cause of R-CPD is not yet clearly understood, but it is believed to be related to the dysfunction of the cricopharyngeus muscle. In Korea, R-CPD is not well understood yet and consequently, there is no available treatment for this condition to date. Here, we aim to report two cases of diagnosing and treating patients with R-CPD for the first time in Korea using botulinum toxin injection under local anesthesia.
서 론
트림을 못하는 증상으로 불편감을 느끼는 사람들이 종종 있으며, 대부분 질병으로 인식하지 못해 병원을 찾지 않고 지내고는 한다. 치료를 위해 병원에 찾아도 이학적 검사 및 임상검사는 모두 정상일 수 있어 이러한 증상은 심리적인 문제로 여겨졌다. 2019년에 Bastian과 Smithson [1]이 광범위한 검사에도 불구하고 특별한 이상소견이 없지만 트림을 못하는 일련의 환자를 발표하였으며, 트림을 못하는 증상과 함께 과도한 복부팽만감과 가슴의 통증, 아랫목과 가슴에서 발생하는 꾸룩거리는 소음, 헛배부름을 특징으로 하는 역행성 윤상인두기능장애(retrograde cricopharyngeus dysfunction)를 처음 명칭하였다. 역행성 윤상인두기능장애의 발생기전은 아직 명확하게 알려진바 없으나 윤상인두근육(cricopharyngeus muscle)의 문제로 생각되어지고 있다. 이에 Bastian은 보툴리늄 독소(botulinum toxin)를 윤상인두근육에 주사하여 역행성 윤상인두기능장애를 치료하였으며, 이후 비슷한 해외의 사례들이 보고되고 있다[2-4]. 그러나 국내에서는 트림을 못하는 질환에 대한 치료나 역행성 윤상인두기능장애에 대해서 알려진 바가 없어 지금까지 이에 대한 치료가 전무하다. 이에 저자들은 국내에서 트림을 못한 환자들을 보툴리늄 독소 주사를 이용해 치료했던 2명의 증례에 대하여 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
증례 1
31세 남자 환자가 어릴 때부터 트림을 못하는 것을 주소로 내원하였다. 항상 손가락으로 구토반사를 유도하여 트림을 했다고 하였다. 음식을 삼킬 때도 꽉 막히는 느낌을 호소하였으나, 삼키는 기능에는 문제가 없었다. 경비식도내시경(transnasal esophagoscopy) 진입 시 저항이 강하게 느껴지는 상부 식도괄약근 과긴장 상태가 확인되었으며, 그 외에 구조적인 이상은 확인되지 않았다(Fig. 1). Eperisone, dexlansoprazole, itopride hydrochloride 투약하며 1달 동안 경과를 보았으나 호전이 없어 보툴리늄 독소 주사를 계획하였다. 시술은 환자의 목에 근전도 전극을 부착한 후 목을 신전시키고 우측을 바라보는 자세로 시행되었다(Fig. 2A). 윤상연골 높이에서 윤상연골과 경동맥 사이 주사부위를 무균적으로 소독한 후 리도카인 국소마취를 시행하였고 보툴리늄 독소 50 단위를 normal saline 1 mL로 희석하여 25 gauge 50 mm의 근전도 주사바늘로 교체하여 준비하였다(Fig. 2B). 바늘을 진입하며 근전도 신호와 소리를 확인하여 윤상인두근육의 위치를 확인하게 되는데 휴식 시 고신호 강도를 나타내고, 침을 삼키면 신호가 소실되는 특징으로 근육의 위치를 확인할 수 있다. 윤상인두근육의 인접한 위치에 성대를 외전시키는 후윤상피열근이 위치하기 때문에 환자에게 들숨을 유도하여 이때 신호가 나타나지 않는지도 확인하여야 한다(Fig. 2C). 윤상인두근육의 위치에 근전도 바늘이 위치함을 확인한 후에 보툴리늄 독소 50단위를 주입하였다. 치료 1달 뒤 부작용으로 음식이 걸리는 느낌이 발생하였고, 트림은 이전보다 잘나왔다. 치료 2달 뒤 부작용은 사라졌으나 트림이 시술 직후 만큼 잘 나오지 않아 추가적으로 보툴리늄 독소 50단위를 주사하였다. 두 번째 치료 후에는 부작용 발생하지 않았으며, 시술 후 6개월까지 경과 관찰하였으나 증상의 재발이 없어 정기적인 추적관찰을 종료하였다.

Trans-nasal esophagoscopy images of patient 1. A: No structural abnormalities at the entrance of the esophagus. B: Upper Esophagus.
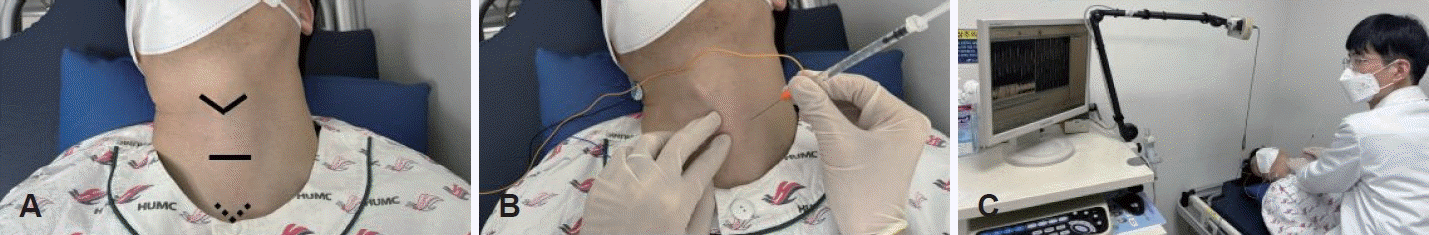
Procedure photos. A: The patient lies down in a supine position after attaching electromyography electrodes to the neck and flexing the neck, while looking to the right. Identify the anatomical structure of the patient’s thyroid cartilage (arrowhead), cricoid cartilage (black line), suprasternal notch (dotted arrowhead). B: By palpating the cricoid cartilage, a needle is inserted between the cricoid cartilage and the carotid artery at the level of the cricoid cartilage. C: While inserting the needle, the position of the cricopharyngeus muscle is confirmed by monitoring electromyography signals and sound. Higher signal intensity results in increased amplitude and louder sound.
증례 2
40세 남자 환자가 어릴 때부터 트림을 잘 못하는 것을 주소로 내원하였다. 무의식적으로 간혹 나오기는 하나 특히 의식적으로 하고자 할 때 할 수 없는 것을 불편감으로 호소하였다. 경비식도내시경 진입 시 저항이 강하게 느껴졌으며, 그 외에 구조적인 이상은 확인되지 않았다(Fig. 3A and B). 식도조영검사(esophagography)상 기관분기부에 열공 의심되는 소견이 있었으며 삼키는 기능에는 문제가 없었다(Fig. 3C and D). 이에 동일한 방법으로 보툴리늄 독소 50단위를 주사하였다. 치료 2주 뒤 트림이 이전보다 잘 나왔으나, 고개를 돌리는 등 특정 자세에서만 잘 나와서 추가 치료를 계획하였다. 치료 1달 뒤 추가적으로 보툴리늄 독소 50단위를 주사하였으며, 이후 트림이 잘 나와서 경과관찰 중이다.
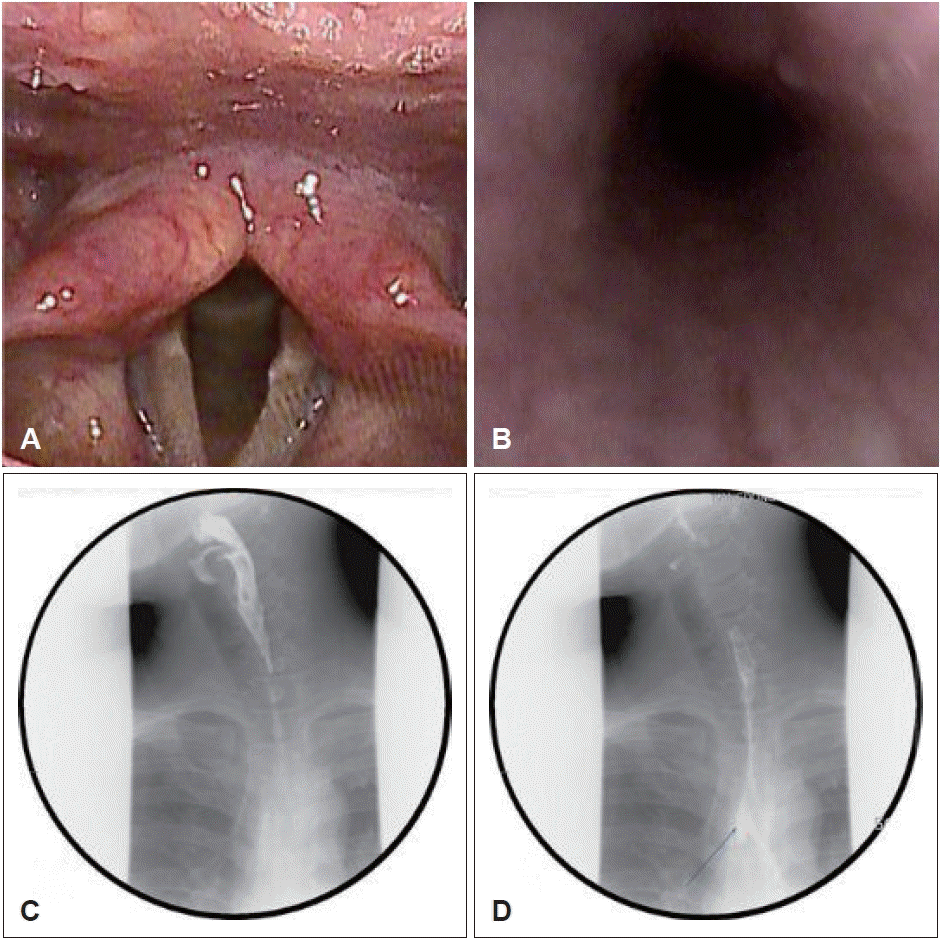
Trans-nasal esophagoscopy images (A and B) and esophagography images (C and D) of patient 2. A: No structural abnormalities at the entrance of the esophagus. B: Upper Esophagus. C: No definite passage disturbance of the upper esophagus. D: The suspected small outpouching lesion at the trachea bifurcation level (blue arrow).
고 찰
트림을 할 수 없는 증상은 소화불량, 과민성 대장증후군과 같은 소화기관의 기능적인 문제나 하인두나 식도 내 종물과 같은 구조적인 문제로 인한 발생할 수 있다. 이러한 문제는 일시적이거나, 구조적인 이상소견을 동반하기에 원인을 확인할 수 있으나, 특별한 원인 없이 지속적으로 트림을 못하는 경우에는 아직까지 명확한 원인이 밝혀지지 않았다. 그렇지만 Bastian과 Smithson [1]은 트림을 못하는 증상이 있는 사람에게 다음과 증후군적 진단 기준을 통해 역행성 윤상인두기능장애로 명명하였다; 1) 트림을 못하는 증상, 2) 과도한 복부팽만감과 가슴의 통증, 3) 아랫목과 가슴에서 발생하는 꾸룩거리는 소음, 4) 헛배부름, 5) 사회적 불편감, 6) 토하기 힘듦. 이들은 이 환자들의 윤상인두근육에 보툴리늄 독소를 주사하였고 모든 환자에서 트림이 호전되었음을 보고하였으며, 보툴리늄 독소 주사가 치료인 동시에 확정적인 진단 검사라고 보고하였다.
보툴리늄 독소 주사 치료의 적응증은 다른 원인이 없으며, Bastian이 제시한 역행성 윤상인두기능장애의 증상이 있고, 이로 인해 생활에 불편감을 느끼며, 치료에 동의하는 경우이다. 치료의 절대적 금기증은 없겠으나 보툴리늄 독소의 민감도는 환자마다 차이가 있을 수 있으며 연축성 발성장애와 같은 기저질환 유무에 따라서도 보툴리늄 독소에 둔감해 치료 효과가 떨어질 수 있다[2]. 성대마비가 있는 환자에서도 보툴리늄 독소의 표적화가 제대로 이루어지지 않을 경우 마비가 악화될 수 있어 상대적 금기증에 속한다. 치료는 크게 두 가지로 나눌 수 있는데 전신마취하에 내시경을 이용하여 인두강 내로 윤상인두근육에 주사하는 방법과[1], 국소마취하에 근전도를 이용하여 윤상인두근육에 경피 주사하는 방법이다[5,6]. 국소마취하에 근전도를 이용한 보툴리늄 독소의 경피 주사는 마취와 관련된 위험도가 적다는 점과 외래에서 시술이 가능하기에 비용-효과적인 점, 필요한 경우 반복적으로 시도할 수 있다는 점에서 효율적이다[7]. 연구마다 차이는 있지만 99% 이상의 환자에게 있어서 1회의 치료만으로도 1주일 이내에 효과가 나타나며, 70% 이상의 환자에게 보툴리늄 독소의 약리학적인 작용 기간인 4개월을 넘어서 증상 완화가 지속적이었다고 보고되고 있다[2,7].
역행성 윤상인두기능장애는 국내에 잘 알려지지 않은 비교적 드문 질병이지만 환자의 삶의 질에 상당한 영향을 초래한다. 저자들은 트림을 못하는 증상으로 내원한 환자들에게 보툴리늄 독소를 진단과 동시에 치료의 목적으로 주사하였으며 증상개선에 효과적이었음을 확인하였다. 다만 본 연구에서는 식도내압검사를 시행하지 않았으며, 질환의 병태생리학적인 기전을 밝히지 못한 점이 한계점이며, 치료의 효과를 예측하기 위해 더 많은 환자를 대상으로 한 추가 연구의 수행을 요한다.
Acknowledgements
None
Notes
Author contributions
Conceptualization: Min Woo Park. Data curation: Sujin Han, Sin Jae Kang. Resources: Sin Jae Kang. Supervision: Min Woo Park. Writing—original draft: Jue Hee Kim. Writing—review & editing: Jue Hee Kim, Min Woo Park.
