서 론
방추세포지방종(spindle cell lipoma)은 양성 지방종양으로 전체 지방 종양에서 약 1.5%를 이루고 있고 경부의 후부, 견부의 상부, 척부에서 호발하며 약 9:1의 비율로 남성에서 흔하게 관찰된다[1]. 비배부 및 비강에서 방추세포지방종이 확인된 경우는 극히 드문 경우로 국내에서는 현재 보고된 사례가 없고 미국 국립생물공학정보센터(National Center for Biotechnology Information) 상에서 총 2 사례만이 보고된 바 있다[1,2]. 방추세포지방종은 방추상세포와 지방조직의 함유도에 따라 그 성질에 차이가 있으며 방추상세포가 주된 비중으로 존재할 경우 그 성질이 단단해지는 특성이 있다. 타 악성, 양성 지방종양과 조직학적으로 유사한 특징을 보여 정확한 병리 진단이 중요하다고 알려져 있고 예후는 비교적 좋은 편으로 일반적으로 국소적 절제를 통해 치료가 가능하다[3]. 본 증례에서는 재발성 방추세포지방종의 절제술 1예에 대해 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
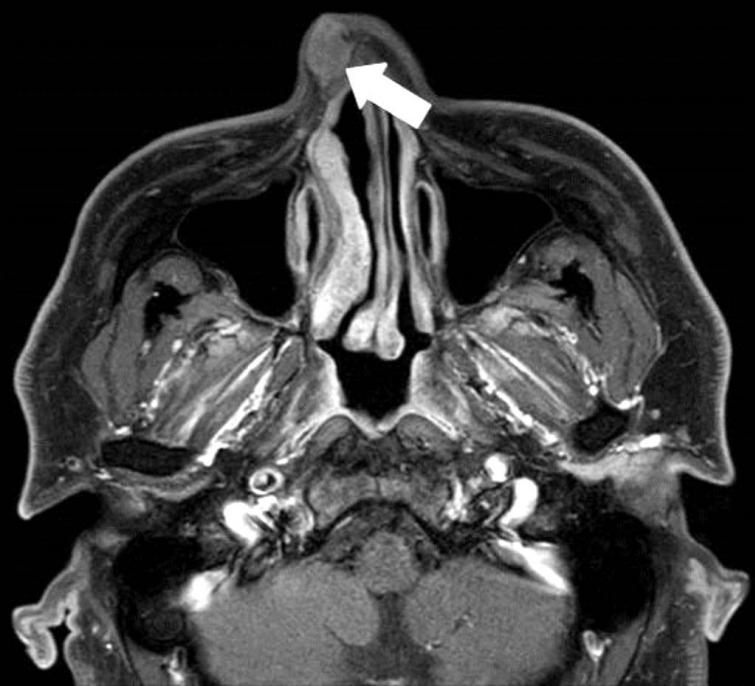
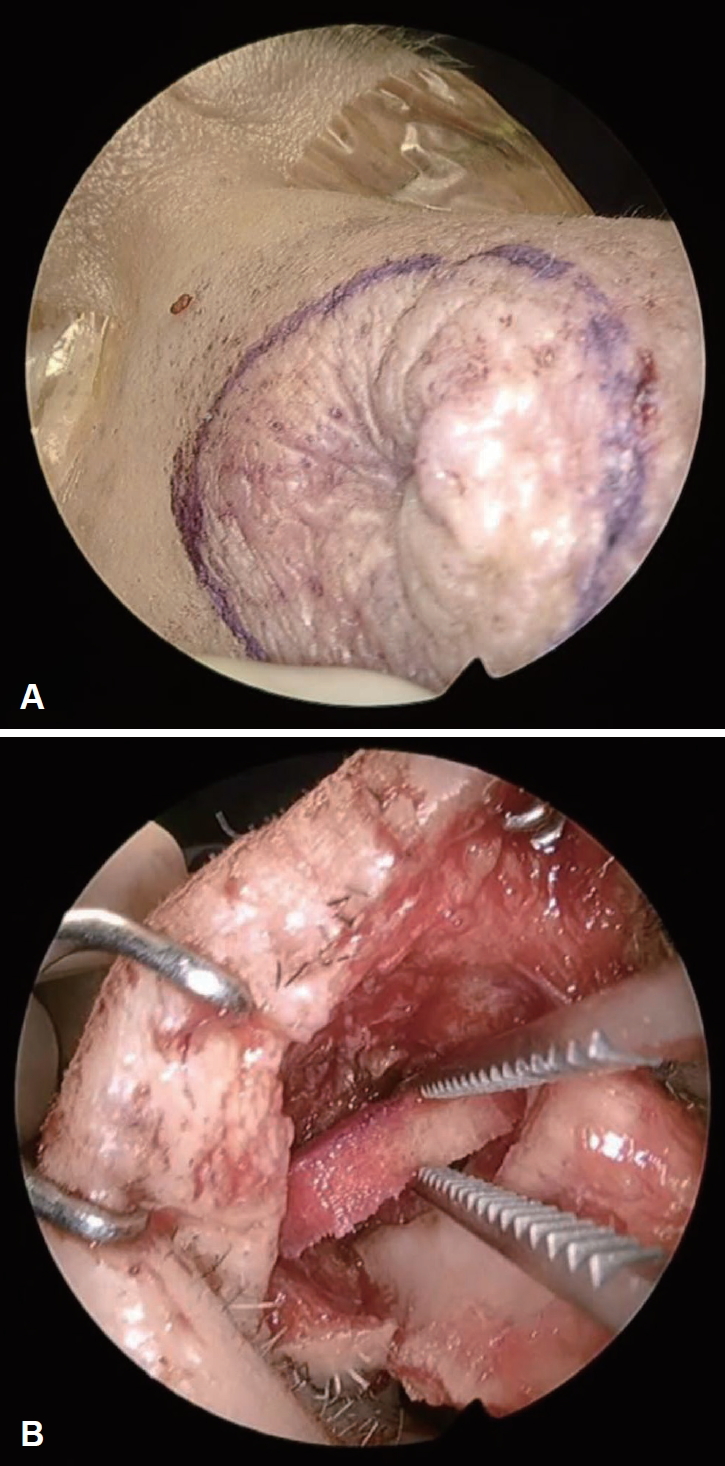
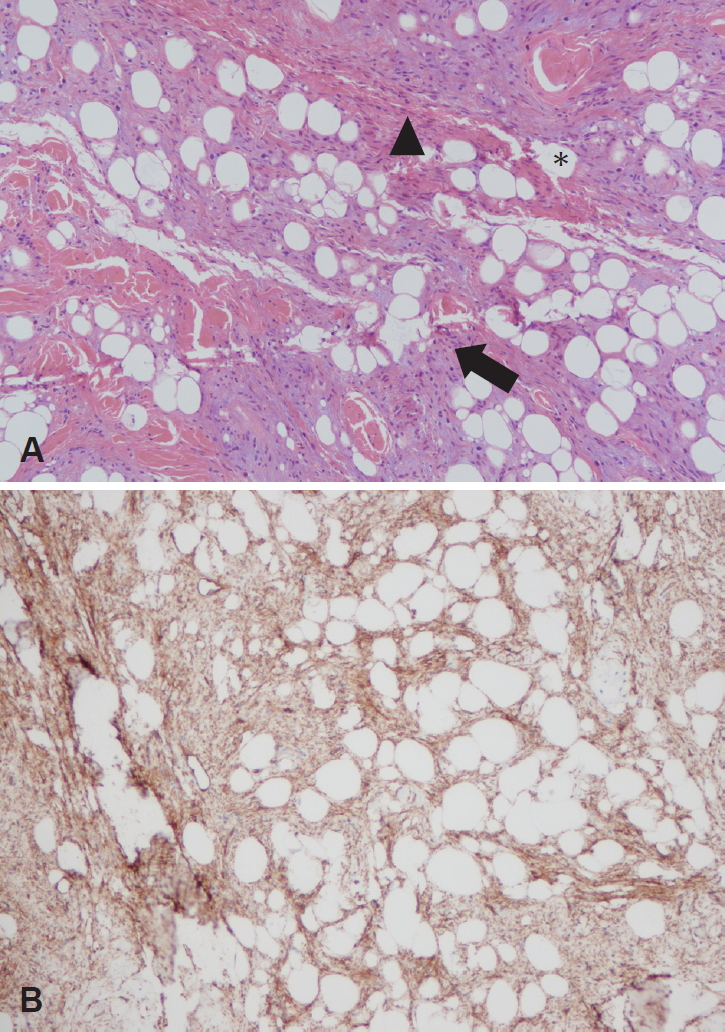
64세 남자가 1년 전부터 발생한 비배부 종물의 지속적인 크기 증가를 보여 내원하였다. 환자는 내원 5년 전 동일 부위 종물로 제거술을 받았으며 당시 진피층에서 결절성 증식 양상의 지방조직 및 방추상세포의 점액성변화(myxoid change)가 관찰되었다. 이외에도 비전형적인 지방성 종양(atypical lipomatous tumor), 점액지방종(myxolipoma), 피부지방종(cutaneous myxoma)과의 감별이 필요했다. 최초 외래 내원 시이학적 소견상 약 0.5×0.5 cm의 부드럽게 촉지되며 압통이 없는 종물이 비배부에서 확인되었고 비내시경 상 특이소견은 발견되지 않았다(Fig. 1). 자기공명영상장치를 통해 T1 강조 음영과 T2 강조음영에서 고신호 강도를 보이면서 비교적 경계가 명확한 1.2×1.5×1.2 cm의 돌출된 종물이 확인되었다. 종물의 내부는 비교적 균일하면서 경계가 불규칙하였고 우측 비강의 배등면에서 피부층과 피하지방층에 걸쳐있었다(Fig. 2). 재발성 종양 의심하에 외접근법을 통해 제거 및 조직검사를 계획하였다. 전신마취 하 비주횡절개(transcolumellar incision)를 통하여 상외측비연골(upper lateral cartilage)에 부착된 비배부의 종물을 확인하여 제거 및 조직검사를 시행하였고 육안 소견 상 1.2×1.5×1.2 cm 크기의 황색과 흰색의 피막이 없는 연조직을 확인하였다. 수술 과정 중 상외측비연골 부위에 1.0×1.0 cm 가량의 결손이 생겼으며 비강을 통하여 무세포 진피 기질(acellular dermal matrix)을 삽입하여 해당 결손부를 보강하였고 비강내에서 봉합술을 실시하였다(Fig. 3). 최종 병리 조직 결과 상 점액성기질이 포함된 방추세포지방종으로 확인되었고 면역염색법 상 CD34에서 양성임이 확인되었으나 S-100에서는 음성이 나타났다(Fig. 4). 술 후 9개월간 외래를 통해 경과 관찰하였고 수술부위의 특이소견이나 재발 소견은 발견되지 않았다(Fig. 5).
고 찰
지방조직에서 기인하는 지방종의 종류로는 맥관지방종(angiolipoma), 골수지방종(myelolipoma), 방추세포지방종(spindle cell lipoma), 연골지방종(chondrolipoma), 점액지방종(myxolipoma) 등이 있다. 방추세포지방종은 전체 지방종에서 약 1.5%의 비중을 차지한다[1]. 현재까지 국내에서는 방추세포지방종이 비강 및 비배부에서 발견된 사례는 보고되지 않았고 구강 및 인후두부에서 발생한 사례만이 드물게 보고되었다[4,5]. 방추세포지방종은 결합 및 연부조직 종양의 일종으로 대개 통증을 동반하지 않으면서 피하층에서 5 cm 미만의 직경으로 나타난다. 주로 두경부에서 나타나고 50대 이상의 남성에서 관찰되는데 이는 해당 병변에서 안드로겐 수용체가 빈번히 발견되기 때문이라는 보고가 있다[6]. 안면부, 안구, 비강, 구강 등에서는 특히 드물게 관찰되고 증상이 없는 경우 치료는 불필요하며 증상이 동반되는 경우 수술적 처치가 필요할 수 있다. 예후는 좋은 편으로 위험인자는 남성 및 50대 이상이라는 조건 이외 확인되지 않았다[7]. 지방종 및 신경종이 국소적 절제를 통해 완치가 가능한 점에서 금번 증례의 지방종과 차이점이 없으나 대부분의 지방종이 여성에서 호발하고, 신체의 특정한 영역에 국한되지 않는 점에서 특정부위에 주로 나타나는 방추세포지방종의 특이점이 있다[3].
영상장치를 통한 방추세포지방종의 진단은 대개 표재성이고 주변 조직과의 경계가 명확한 것을 확인할 수 있다는 점을 제외하고는 유용하지 않다. 방추세포지방종을 육안으로 확인하였을 경우 그 경계가 대체로 명확하며, 단면을 절제하였을 때 지방조직과 방추상세포의 함유 정도에 따라 황색에서 백색까지 다양하게 나타난다[8]. 타 지방종과의 조직학적 감별이 어려워 지방 조직의 함유정도가 낮은 경우 확진이 어려울 수 있다. 해당 종양에서 호산구성 콜라겐섬유다발(eosinophilic ropy collagen bundle), 비만세포(mast cell)도 조직학적으로 확인될 수 있으며 이번 사례에서처럼 드물게 점액성 기질이 풍부하게 나타나는 경우도 있다[9]. 양성 신경초종과 조직학적 형태가 유사하여 특히 신경섬유종(neurofibroma)과 신경초종(schwannoma)과의 감별진단이 필요하다[10]. 이를 감별하기 위해 특정 염색에 대해 양성인 점을 이용하는데 방추상세포는 양성 안드로겐수용체 중 하나인 CD34에 양성이고[11], 성숙한 지방세포는 대개 S-100에 양성을 보인다[12]. 병리학적으로 방추세포지방종과 유사한 다형선종(pleomorphic adenoma)은 콜라겐의 밀집도가 높고 거대세포(giant cell)가 관찰된다는 점에서 금번 증례의 경우와 차이가 있고, 점액지방종은 짧은 방추상세포(short spindle smaller cell)가 관찰되며 방추세포지방종과 조직학적 구조가 유사하나 CD34에서 음성을 보이는 점에서 차이가 있다[13].
본 증례는 비배부의 피하층에서 종양이 확인되었다는 점과 5년전 동일한 부위에서 진피층의 지방조직과 결절성 증식으로 진단력이 있는 점에서도 특이점이 있다. 조직학적 결과상 방추상세포에 성숙한 지방세포의 혼합양식으로 고전적인 양상의 방추세포지방종의 병리학적 소견이 나타난다. 가늘고 긴 양상의 세포질 형태에 점액성 기질이 관찰되었고 이러한 양상의 병리학적 소견은 5년전 슬라이드와 비교하여 유사함을 확인하였다. Kim 등[14]이 방추상세포의 암화(carcinogenesis)에 대해 다룬 바 있지만 방추상세포 편평상피암(squamous cell carcinoma)에 국한하여 보고되었고 방추상세포 지방종으로의 암화는 현재 보고된 바가 없다. 따라서 이전 지방조직과 방추상세포의 조직학적 변이를 배제할 수 없으나 가능성은 희박할 것으로 보인다. 5년전 병리학적 진단에 제한이 있을 수 있으며 완전 절제가 이루어지지 않았던 조직의 재발 가능성을 의심해 볼 수 있다. 방추세포지방종이 근육내로 침윤한 경우 수술적 절제를 하였음에도 재발하였다는 보고가 있지만 대부분 방추세포지방종은 비교적 예후가 좋고 수술적 절제를 시행한 경우 재발 가능성은 떨어진다고 알려져 있다[15]. 이번 사례에서는 외비접근법에 의한 코성형술을 통해 성공적으로 병변을 절제하였고 무세포 진피 기질을 이용하여 결손부를 보강하였다. 술 후 9개월이 경과한 시점까지 수술부위의 재발 및 특이소견은 관찰되지 않았다.