 |
 |
AbstractBackground and ObjectivesNeurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized as bilateral vestibular schwannoma (VS), various brain and spinal tumors. This study is aimed to investigate the relationship between the genotypes and phenotypes of NF2 found in the Korean population.
Subjects and MethodWe retrospectively reviewed 11 patients who were diagnosed with NF2 and observed them for more than a year. NF2 gene mutations were detected using Sanger sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). The mutations were classified into tissue mosaicism, classic, and severe genotypes according to the UK NF2 genetic severity score. Tumor load was assessed by reviewing MR images and audiological findings were analyzed.
ResultsWe identified 7 cases (63.6%) of mutations from 11 patients who were diagnosed with NF2. While three patients showed classic and four showed severe genotypes, four patients were presumed as tissue mosaicism. The patients with severe genotypes didnвҖҷt show more severe clinical manifestations in terms of tumor load and hearing. Four patients with tissue mosaicism were detected in the older age group than those with mutation. Of the five patients who had serviceable bilateral hearing at the initial diagnosis, all maintained their serviceable hearing during the follow-up.
м„ң лЎм ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ(neurofibromatosis type 2, NF2)мқҖ 22лІҲ м—јмғүмІҙм—җ мһҲлҠ” NF2 мў…м–‘ м–өм ң мң м „мһҗмқҳ ліҖмқҙлЎң мқён•ҙ л§җмҙҲмӢ кІҪ лҳҗлҠ” мӨ‘추мӢ кІҪ мЎ°м§Ғм—җм„ң лӢӨл°ңм„ұ мў…м–‘мқҙ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” л§Өмҡ° л“ңл¬ё м§ҲнҷҳмқҙлӢӨ. мғҒм—јмғүмІҙ мҡ°м„ұмңјлЎң мң м „лҗҳлҠ” м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҖ м•Ҫ 60000лӘ…лӢ№ 1лӘ… м •лҸ„мқҳ мң лі‘лҘ мқ„ ліҙмқҙл©°[1], мқҙ м§Ҳнҷҳм—җ мқҙнҷҳлҗң нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ мӢ кІҪкі„, лҲҲ, н”јл¶Җ лі‘ліҖмқҙ л°ңмғқн•ҳкІҢ лҗңлӢӨ. м–‘мёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…(vestibular schwannoma)мқҖ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң к°ҖмһҘ нқ”н•ҳкІҢ ліҙмқҙлҠ” мһ„мғҒ м–‘мғҒмқҙлӮҳ лӢӨлҘё лҮҢмӢ кІҪ, мІҷмҲҳмӢ кІҪ, л§җмҙҲмӢ кІҪм—җм„ңлҸ„ мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…(schwannoma)мқҙ л°ңмғқн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. м–‘мёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқҙ мһҲкұ°лӮҳ, мқјмёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқё кІҪмҡ°м—җлҸ„ мҲҳл§үмў…(meningioma), мӢ кІҪкөҗмў…(glioma), мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…(neurofibroma), л°ұлӮҙмһҘ(cataract)мқҙ мһҲлҠ” кІҪмҡ° м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмңјлЎң 진лӢЁн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. мһҗм„ён•ң 진лӢЁ кё°мӨҖмқҖ Table 1м—җ кё°мҲ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ[2,3].
мҳҒкөӯмқҳ мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳ(Genetic Severity Score) м§Җн‘ңлҠ” м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ мң м „мһҗнҳ•м—җ л”°лқј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқ„ 분лҘҳн•ң кІғмқҙлӢӨ(Table 2). лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙм—җ л”°лқјм„ң мЎ°м§Ғ м„һмһ„мҰқ(tissue mosaicism), м „нҳ•м Ғ(classic), мӨ‘мҰқ(severe)мқҳ м„ё к°Җм§Җ 분лҘҳлЎң лӮҳлҲ„л©°, м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ мҳҲнӣ„лҘј 추측н•ҳм—¬ нҷҳмһҗлҘј мғҒлӢҙн•ҳкұ°лӮҳ мҲҳмҲ м Ғ мІҳм№ҳлӮҳ м •мң„м Ғ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј кІ°м •н• л•Ң м°ёкі м§Җн‘ңлЎң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ңлӢӨ[4].
лҜёкөӯкіј мң лҹҪм—җм„ңлҠ” м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҳ мң м „нҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ мһҳ к·ңлӘ…лҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлӢӨ. мқјл°ҳм ҒмңјлЎң м ҲлӢЁнҳ• лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ(truncating mutation)лҘј к°Җм§ҲмҲҳлЎқ мӢ¬н•ң мһ„мғҒ мҰқмғҒмқҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳл©°, м ҲлӢЁл¶Җ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ(splice site mutation), мІҙм„ёнҸ¬ м„һмһ„мҰқ(somatic mosaicism), кіјмҳӨ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ(missense mutation)мқё кІҪмҡ° мғҒлҢҖм ҒмңјлЎң лҠҰмқҖ лӮҳмқҙм—җ мҰқмғҒмқҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳлҠ” нҺёмқҙлқј м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[5-9].
м Җмһҗл“Өмқҙ мЎ°мӮ¬н•ң л°”м—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ, м•„мӢңм•„м—җм„ңлҠ” м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҳ мң м „нҳ•мқҙ мғҲлЎӯкІҢ ліҙкі лҗң кІғ мҷём—җлҠ” мң м „нҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ м—°кө¬лҗң мһҗлЈҢлҠ” м—ҶлҠ” мғҒнғңмқҙлӢӨ. мқҙм—җ ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳ м§Җн‘ңлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ н•ңкөӯм—җм„ңмқҳ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ мң м „нҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ• мӮ¬мқҙмқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқ„ м•Ңм•„ліҙкі мһҗ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
лҢҖмғҒ л°Ҹ л°©лІ•лҢҖ мғҒ2010л…„ 1мӣ”~2020л…„ 5мӣ”к№Ңм§Җ мҲңмІңн–ҘлҢҖн•ҷкөҗ л¶ҖмІңлі‘мӣҗ мқҙ비мқёнӣ„кіјм—җ лӮҙмӣҗн•ң нҷҳмһҗ мӨ‘ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмңјлЎң 진лӢЁл°ӣмқҖ нҷҳмһҗ 27лӘ…мқҳ мқҳл¬ҙкё°лЎқкіј мң м „мһҗ кІҖмӮ¬ кІ°кіјлҘј нӣ„н–Ҙм ҒмңјлЎң 분м„қн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙл“Ө мӨ‘ мҳҒмғҒмқҳн•ҷм Ғ кІҖмӮ¬лҘј нҶөн•ҙ м–‘мёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗң нҷҳмһҗ мӨ‘ 1л…„ мқҙмғҒ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°°н•ң нҷҳмһҗлҘј нҸ¬н•Ён•ҳмҳҖкі , мқјмёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқ„ к°–кі мһҲкұ°лӮҳ мң м „мһҗ кІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ м ңмҷён•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. к°Ғ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мҷёлһҳ лӮҙмӣҗ лӢ№мӢң мЈј мҰқмғҒ, мІҳмқҢ 진лӢЁлҗң лӮ м§ң, мІӯл ҘкІҖмӮ¬, мҳҒмғҒмқҳн•ҷм Ғ кІҖмӮ¬ кІ°кіј, м•Ҳкіј 진лЈҢкё°лЎқм§Җ л“ұмқҳ мқҳл¬ҙкё°лЎқмқ„ нҶөн•ҙ мЎ°мӮ¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. ліё м—°кө¬лҠ” ліёмӣҗ м—°кө¬мңӨлҰ¬ мӢ¬мқҳ мң„мӣҗнҡҢ(Institutional Review Board, IRB)мқҳ мҠ№мқёмқ„ л°ӣм•„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(IRB No. 2020-08-018).
мң м „мһҗ кІҖмӮ¬к°Ғ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ л§җмҙҲ нҳҲм•Ўмқ„ мұ„м·Ён•ҳм—¬ мң м „мһҗ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ кІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–ү нӣ„ мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳм—җ л”°лқј 분лҘҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ кІҖмӮ¬лҠ” м§Ғм ‘ DNA м—јкё°м„ңм—ҙкІҖмӮ¬(direct DNA sequencing)мҷҖ лӢӨмӨ‘кІ°м°°мқҳмЎҙ н”„лЎңлёҢ мҰқнҸӯ(multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification, MLPA)мқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
м§Ғм ‘ DNA м—јкё°м„ңм—ҙкІҖмӮ¬лҠ” нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ л§җмҙҲнҳҲм•ЎмңјлЎңл¶Җн„° м–»мқҖ л°ұнҳҲкө¬мқҳ DNAлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. Wizardв“Ү Genomic DNA Purification Kit(Promega, Madison, WI, USA)лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ 추м¶ңлҗң DNAлҠ” м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ мң м „мһҗмқҳ м „мІҙ мҪ”л”© мҳҒм—ӯ(exon 1-16)кіј м—‘мҶҗ-мқёнҠёлЎ (exon-intron) кІҪкі„лҘј м Ғм Ҳн•ң мӢңлҸҷмІҙ м„ёнҠё(primer set)лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ мӨ‘н•© нҡЁмҶҢ м—°мҮ„л°ҳмқ‘(polymerase chain reaction)мңјлЎң мҰқнҸӯмӢңмј°лӢӨ. к°Ғ мӨ‘н•© нҡЁмҶҢ м—°мҮ„ л°ҳмқ‘ мӮ°л¬јл“ӨмқҖ BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit(Applied Biosystems, Rotkreuz, Switzerland)лЎң мҲңнҷҳ мҲңм„ң кІ°м •(cycle sequencing) нӣ„ ABI Prism 3130 Genetic Analyzer(Applied Biosystems)мңјлЎң м „кё°мҳҒлҸҷмқ„ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. л°ңкІ¬лҗң мң м „мһҗ ліҖмқҙлҠ” DNA sequence assembly software Sequencher 4.10.1(Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI, USA)мқ„ мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ 분м„қн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, GenBankмқҳ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ мӢңнҖҖмҠӨ(GenBank ID NM_000268.3)лҘј м°ёмЎ°м„ңм—ҙлЎң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ м„ңм—ҙмқҙ л°ңкІ¬лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡкұ°лӮҳ, мӨ‘н•© нҡЁмҶҢ м—°мҮ„л°ҳмқ‘мқҙ мӢӨнҢЁн•ң кІҪмҡ°, нҒ° лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙ(large mutation)лҘј нҷ•мқён•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ, SALSA P044-NF2 Kit(MRC-Holland, Amsterdam, Netherlands)мқ„ мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ лӢӨмӨ‘кІ°м°°мқҳмЎҙ н”„лЎңлёҢ мҰқнҸӯ(MLPA)мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. ABI 9700 Thermal Cycler(Model 9700; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA)лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ н”„лЎңлёҢ нҳјн•©л¬јкіј көҗмһЎн•ҳм—¬ кІ°н•©мӢңнӮЁ нӣ„ мӨ‘н•© нҡЁмҶҢ м—°мҮ„л°ҳмқ‘ мҰқнҸӯмқ„ н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, мӨ‘н•© нҡЁмҶҢ м—°мҮ„л°ҳмқ‘ мҰқнҸӯ мӮ°л¬јмқҖ ABI Prism 3130xl Genetic Analyzer(Applied biosystems)лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ м „кё°мҳҒлҸҷмқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳкі GeneMarker 1.9 software(SoftGenetics, LLC, State College, PA, USA)лҘј нҶөн•ҙ 분м„қн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мІӯл ҘкІҖмӮ¬лӘЁл“ нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ лӮҙмӣҗ лӢ№мӢң мҲңмқҢмІӯл ҘкІҖмӮ¬мҷҖ м–ҙмқҢлӘ…лЈҢлҸ„кІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, мҲңмқҢмІӯл ҘкІҖмӮ¬лҠ” 0.5, 1, 2, 3 kHz мЈјнҢҢмҲҳмқҳ мІӯл Ҙм—ӯм№ҳмқҳ нҸүк· мңјлЎң кі„мӮ°н•ҳмҳҖкі , м–ҙмқҢлӘ…лЈҢлҸ„кІҖмӮ¬лҠ” лӢЁмқҢм Ҳ лӢЁм–ҙ лӘ©лЎқмқ„ нҷҳмһҗм—җкІҢ мқҪкІҢ н•ң л’Ө м •нҷ•нһҲ л°ңмқҢн•ң кІҪмҡ°лҘј нҚјм„јнҠёлЎң н‘ңмӢңн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. к°Ғ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ мҲңмқҢм—ӯм№ҳнҸүк· кіј м–ҙмқҢлӘ…лЈҢлҸ„ мҲҳм№ҳлҠ” American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery(AAO-HNS) 분лҘҳлІ•мқ„ мқҙмҡ©н•ҙ A, B, C, Dкө°мңјлЎң 분лҘҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Fig. 1) [10]. мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл ҘмқҖ AAO-HNS 분лҘҳлІ•м—җм„ң мҲңмқҢм—ӯм№ҳнҸүк· мқҙ 50 dB HL лҜёл§Ңмқҙкі , м–ҙмқҢлӘ…лЈҢлҸ„к°Җ 50%лҘј мҙҲкіјн•ҳлҠ” Aкө°кіј Bкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳлҠ” кө¬к°„мқҳ мІӯл ҘмңјлЎң м •мқҳн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мҳҒмғҒкІҖмӮ¬ л°Ҹ м•Ҳкіј 진лЈҢ кё°лЎқл¶Җ нҷ•мқёнҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ мІ« лӮҙмӣҗ лӢ№мӢң мЎ°мҳҒмҰқк°• мёЎл‘җкіЁ мһҗкё°кіөлӘ…мҳҒмғҒкіј мЎ°мҳҒмҰқк°• мІҷ추 мһҗкё°кіөлӘ…мҳҒмғҒмқ„ мҙ¬мҳҒн•ҳм—¬, м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқҙлӮҳ мҲҳл§үмў…, мІҷ추종양 л“ұмқҙ мһҲлҠ”м§Җ нҸүк°Җн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ мөңмҙҲ лӮҙмӣҗ лӢ№мӢңл¶Җн„° мЈјкё°м Ғмқё м•ҲкіјкІҖ진мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳм—¬ л°ұлӮҙмһҘ, мӢңмӢ кІҪмҲҳл§үмў…(optic nerve meningioma), л§қл§үм „л§ү(epiretinal membrane), мӢңмӢ кІҪкөҗмў…(optic nerve glioma), л§қл§үкіјмҳӨмў…(retinal harmatoma) л“ұмқҳ м—¬л¶ҖлҘј нҷ•мқён•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
кІ° кіј27лӘ…мқҳ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“Ө мӨ‘ ліё м—°кө¬м—җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗң нҷҳмһҗлҠ” мҙқ 11лӘ…мңјлЎң, 2лӘ…мқҖ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ к°ҖмЎұл Ҙмқҙ мһҲм—Ҳкі (мӮ¬лЎҖ 8лІҲ, 10лІҲ), к·ё мҷё 9лӘ…мқҖ мӮ°л°ңм Ғ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. нҷҳмһҗ м—°л №мқҖ 6~47м„ёлЎң лӢӨм–‘н•ҳкІҢ 분нҸ¬н•ҳмҳҖкі нҸүк· нҳ„мһ¬ м—°л №мқҖ 24.9м„ёмҳҖмңјл©°, мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢң нҸүк· м—°л №мқҖ 21.6м„ёмҳҖлӢӨ. лӮЁл…Җ 비мңЁмқҖ 6:5лЎң 비мҠ·н•ҳмҳҖкі , нҸүк· м¶”м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„мқҖ м•Ҫ 33к°ңмӣ”мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. м–‘мёЎ мІӯл Ҙм—ӯм№ҳлҘј 비көҗн•ҳм—¬ мўӢмқҖ к·Җ(better ear)лҘј лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н–Ҳмқ„ л•Ң, AAO-HNS кё°мӨҖ Aкө°мқҖ 8лӘ…, Bкө°мқҖ 3лӘ…, Cкө°кіј Dкө°мқҖ к°Ғк°Ғ 0лӘ…мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ.
мң м „мһҗ кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” 11лӘ… мӨ‘ 7лӘ…мқҳ нҳҲм•Ўм—җм„ң лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙк°Җ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. м—‘мҶҗ 2-13м—җ м ҲлӢЁнҳ• лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙк°Җ мһҲлҠ” нҷҳмһҗ 4лӘ…, м—‘мҶҗ 1-7м—җ м ҲлӢЁл¶Җ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙк°Җ мһҲлҠ” нҷҳмһҗ 2лӘ…, к·ёлҰ¬кі н”„лЎңлӘЁн„°(promotor)лӮҳ м—‘мҶҗ 1м—җ кІ°мҶҗ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙк°Җ мһҲлҠ” нҷҳмһҗк°Җ 1лӘ…мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. 11лӘ… мӨ‘ 2лӘ…мқ„ м ңмҷён•ҳкі 9лӘ…мқҳ м–‘мёЎ мІӯл Ҙмқҙ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң, 11лӘ… мӨ‘ 6лӘ…м—җкІҢм„ң м–‘мёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў… мҷём—җ мІҷ추종양мқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Table 3).
мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳм—җ л”°лқј нҷҳмһҗлҘј лӮҳлҲ„м—Ҳмқ„ л•Ң(Table 4), к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җлҠ” 4лӘ…мқҳ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм—Ҳкі нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ 진лӢЁ лӢ№мӢңмқҳ нҸүк· м—°л №мқҖ 33.3м„ёмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙл“Ө мӨ‘ 2лӘ…мқҙ м–‘мёЎ к·Җ лӘЁл‘җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ к°Җм§Җкі мһҲм—Ҳкі , лӮҳлЁём§Җ 2лӘ…мқҖ мқјмёЎм—җм„ңл§Ң мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙл“Ө мӨ‘ н•ң лӘ…мқҙ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ AAO-HNS кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң м–‘мёЎ к·Җ лӘЁл‘җ Dкө°мңјлЎң мІӯл Ҙмқҙ м Җн•ҳлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Fig. 2).
к·ёлЈ№ 2Aм—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳлҠ” нҷҳмһҗлҠ” 1лӘ…мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. мқҙ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢңмқҳ м—°л №мқҖ 15.0м„ёмҳҖмңјл©°, мІӯл ҘмқҖ AAO-HNS Bкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ.
к·ёлЈ№ 2Bм—җлҠ” 2лӘ…мқҙ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм—Ҳкі м§„лӢЁ лӢ№мӢңмқҳ м—°л №мқҖ к°Ғк°Ғ 3м„ё, 30м„ёмҳҖлӢӨ. 2лӘ…мқҳ лӘЁл‘җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ.
к·ёлЈ№ 3м—җлҠ” 4лӘ…мқҳ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢңмқҳ нҸүк· м—°л №мқҖ 14.3м„ёмҳҖмңјл©°, мІӯл ҘмқҖ 4лӘ… лӘЁл‘җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Fig. 3).
к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җм„ңл§Ң мӢңл Ҙм Җн•ҳмҷҖ л°ұлӮҙмһҘ л“ұмқҳ м•Ҳкіјм Ғ мҰқмғҒмқҙ лҸҷл°ҳлҗң нҷҳмһҗк°Җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. мҳҒмғҒмқҳн•ҷм Ғ кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗң 4лӘ… лӘЁл‘җ мІҷ추종양мқҙ лҸҷл°ҳлҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°, к·ёлЈ№ 2BмҷҖ к·ёлЈ№ 3м—җм„ңлҠ” к°Ғк°Ғ н•ң лӘ…м”©л§Ң л°ңкІ¬лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ.
мІ« мІӯл ҘкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң 17м„ё мқҙмғҒмқҙл©°, м–‘мёЎ к·Җ лӘЁл‘җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗң 5лӘ…мқҖ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мң м§Җн–ҲлӢӨ. 진лӢЁ мӢң н•ңмӘҪ к·ҖлқјлҸ„ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” нҷҳмһҗлҠ” 2лӘ…мқҙ мһҲм—Ҳкі лӘЁл‘җ к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳмҳҖлҠ”лҚ°, мқҙл“ӨмқҖ лӘЁл‘җ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ мІӯл Ҙм Җн•ҳ мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ.
кі м°°м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҖ 22лІҲ м—јмғүмІҙмқҳ мһҘмҷ„м—җ мң„м№ҳн•ң NF2 мң м „мһҗмқҳ лҸҢм—°ліҖмқҙлЎң мқён•ҙ л°ңмғқн•ңлӢӨ. NF2 мң м „мһҗлҠ” л©ҖлҰ°(merlin)мқҙлқј л¶ҲлҰ¬лҠ” мў…м–‘м–өм ң лӢЁл°ұм§Ҳмқ„ кө¬м„ұн•ҳлҠ”лҚ°, мӢ кІҪкі„ лӮҙмқҳ мҠҲл°ҳм„ёнҸ¬м—җм„ң мғқм„ұлҗҳлҠ” л©ҖлҰ°мқҖ м„ёнҸ¬к°Җ л№ лҘё мҶҚлҸ„лЎң м„ұмһҘн•ҳкұ°лӮҳ л¶„н• н•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳкІҢ мЎ°м Ҳн•ҳлҠ” м—ӯн• мқ„ н•ңлӢӨ. NF2 мң м „мһҗк°Җ ліҖнҳ•лҗҳл©ҙ л©ҖлҰ°мқҙ м •мғҒм Ғмқё кё°лҠҘмқ„ мҲҳн–үн•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҙ м„ёнҸ¬к°Җ л№ лҘҙкІҢ м„ұмһҘн•ҳкі л¶„м—ҙн•ҳм—¬ м–‘м„ұмў…м–‘мқ„ л°ңмғқмӢңнӮЁлӢӨ. м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ м•Ҫ 95%м—җм„ң м–‘мёЎм„ұ м „м •мӢ кІҪмҙҲмў…мқҙ л°ңмғқн•ңлӢӨкі м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲмңјл©°, лӮңмІӯ, мқҙлӘ…, м–ҙм§ҖлҹјмҰқмқ„ мЈјлЎң нҳёмҶҢн•ңлӢӨ. ліё м—°кө¬м—җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗң нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җм„ңлҸ„ м Ҳл°ҳ мқҙмғҒм—җм„ң лӮңмІӯ, мқҙлӘ… л“ұмқҳ к·Җ мҰқмғҒл“Өмқ„ мЈј мҰқмғҒмңјлЎң нҳёмҶҢн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ 섬мң мў…мҰқмқҖ м№ҳлЈҢ л°©м№Ёмқ„ кІ°м •н•ҳкё° л§Өмҡ° м–ҙл Өмҡҙ м§Ҳлі‘мқҙлӢӨ. мң м „мһҗнҳ•-н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„м—җ лҢҖн•ң м—°кө¬л“Өмқ„ кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мң м „нҳ•м—җ к·јкұ°н•ң мҳҲнӣ„ мҳҲмёЎмқҖ лҸ„мӣҖмқҙ лҗ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. мҳҒкөӯмқҳ мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ 진н–үлҗң м„ н–ү м—°кө¬м—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„мҷҖ мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢңмқҳ лӮҳмқҙмҷҖ нҳ„мһ¬ лӮҳмқҙлҠ” мқҢмқҳ мғҒкҙҖкҙҖкі„лҘј к°Җм§Җл©°, мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢң нҸүк· лӮҳмқҙлҠ” к·ёлЈ№ 1мқҳ кІҪмҡ° 47.0м„ё, к·ёлЈ№ 3мқҳ кІҪмҡ° 15.9м„ёлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„к°Җ лҶ’мқҖ к·ёлЈ№мқјмҲҳлЎқ мІҷ추종양мқҳ л°ңкІ¬ л№ҲлҸ„к°Җ лҶ’м•ҳмңјл©°, м•Ҳкіјм Ғ м§Ҳнҷҳкіј мІӯл Ҙм Җн•ҳ лҳҗн•ң м„ нҳ• кІҪн–Ҙм„ұмқ„ ліҙмқёлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[4].
ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” к·ёлЈ№ 1мқҳ мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢң нҸүк· м—°л №мқҖ 33.3м„ё, к·ёлЈ№ 3мқҳ мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢң нҸүк· м—°л №мқҖ 14.3м„ёлЎң м•һм„ м—°кө¬мҷҖ 비мҠ·н•ң кІҪн–Ҙм„ұмқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ. к·ёлҹ¬лӮҳ мІӯл Ҙмқҳ кІҪмҡ° к·ёлЈ№ 3м—җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗң 4лӘ… лӘЁл‘җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ к°Җм§Җкі мһҲм—Ҳмңјл©°, мҳӨнһҲл Ө к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җм„ң мқјмёЎмқҳ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙм—җ нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” мІӯл Ҙмқ„ к°Җ진 нҷҳмһҗк°Җ л‘җ лӘ… нҸ¬н•Ёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. м•Ҳкіјм Ғ м§Ҳнҷҳмқ„ к°Җ진 нҷҳмһҗлҠ” к·ёлЈ№ 1м—җм„ңл§Ң л°ңкІ¬лҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°, к·ёлЈ№ 1мқҳ нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җкІҢм„ң лӘЁл‘җ мІҷ추종양мқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм–ҙ, 1лӘ…м—җкІҢм„ңл§Ң мІҷ추종양л§Ң нҷ•мқёлҗң к·ёлЈ№ 3кіјлҠ” лҢҖ비лҗҳлҠ” лӘЁмҠөмқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ. м „мІҙм ҒмңјлЎң к·ёлЈ№ 1 нҷҳмһҗкө°мқҙ к·ёлЈ№ 3 нҷҳмһҗкө°ліҙлӢӨ мӢ¬к°Ғн•ң мһ„мғҒм–‘мғҒмқ„ ліҙм—¬, кё°мЎҙ ліҙкі лҗң м—°кө¬мқҳ кІ°кіјмҷҖлҠ” лӢӨлҘё кІҪн–Ҙм„ұмқ„ лқ м—ҲлӢӨ.
мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳмҷҖ мІӯл Ҙмқҳ кҙҖкі„лҘј м—°кө¬н•ң лӢӨлҘё н•ң м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳм—җ л”°лқј, мЎ°м§Ғ м„һмһ„мҰқ к·ёлЈ№м—җм„ңлҠ” AAO-HNS Aкө°мқё нҷҳмһҗк°Җ 64% к°Җлҹү лҗҳм—ҲмңјлӮҳ, мӨ‘мҰқ к·ёлЈ№м—җм„ңлҠ” м Ҳл°ҳ мқҙмғҒмқҳ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мһғм–ҙлІ„л ёкі , 35%л§Ңмқҙ AAO-HNS Aкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[11]. ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ңлҠ” мЎ°м§Ғ м„һмһ„мҰқ к·ёлЈ№ мӨ‘ AAO-HNS Aкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳлҠ” нҷҳмһҗлҠ” 4лӘ… мӨ‘ 2лӘ…, мӨ‘мҰқ к·ёлЈ№м—җм„ң Aкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№н•ҳлҠ” нҷҳмһҗлҠ” 4лӘ… мӨ‘ 4лӘ…мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. мқҙлҠ” кё°мЎҙ м—°кө¬мҷҖ м°Ёмқҙм җмқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ” кІ°кіјмқҙлӮҳ лҢҖмғҒ нҷҳмһҗ мҲҳк°Җ м Ғм–ҙ 추к°Җм Ғмқё м—°кө¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң ліҙмқёлӢӨ.
мқҙм „ м—°кө¬м—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ лӮҳмқҙк°Җ л“Өм–ҙк°җм—җ л”°лқј мІӯл Ҙмқҙ л–Ём–ҙм§ҖлҠ” лӘЁмҠөмқ„ ліҙмқҙлҠ”лҚ°, мЎ°м§Ғ м„һмһ„мҰқ к·ёлЈ№мқҳ нҷҳмһҗл“Ө мӨ‘ м Ҳл°ҳмқҖ 80м„ёк№Ңм§Җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мң м§Җн•ҳлӮҳ кІҪлҸ„мҷҖ мӨ‘л“ұлҸ„ к·ёлЈ№м—җм„ңлҠ” 44~46м„ё, мӨ‘мҰқ к·ёлЈ№м—җм„ңлҠ” 32м„ём—җ м Ҳл°ҳмқҳ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мһғм–ҙлІ„лҰ°лӢӨкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ[11].
ліё м—°кө¬м—җм„ң мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢң 17м„ё мқҙмғҒмқҙл©° м–‘мёЎ к·Җ лӘЁл‘җ AAO-HNS Aкө°м—җ н•ҙлӢ№лҗң 5лӘ…мқҖ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ м •мғҒмІӯл Ҙмқ„ мң м§Җн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©° к°ҖмһҘ кёҙ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°° кё°к°„мқҖ 35к°ңмӣ”мқҙм—ҲлӢӨ. мқҙм „ м—°кө¬кІ°кіјмҷҖ лӢӨлҘҙкІҢ м—°л №м—җ л”°лқј мІӯл Ҙм Җн•ҳк°Җ 진н–үлҗҳлҠ” лӘЁмҠөмқ„ ліҙмқҙм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳмңјлӮҳ, нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ лӮҳмқҙк°Җ мқҙм „ м—°кө¬мқҳ к°Ғ кө°м—җ л”°лҘё мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мһғм–ҙлІ„лҰ¬лҠ” нҸүк· м—°л №лҢҖм—җ лҜём№ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳлҜҖлЎң ліҙлӢӨ мһҘкё°к°„мқҳ 추м Ғ кҙҖм°°мқҙ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң ліҙмқёлӢӨ.
ліё м—°кө¬лҠ” лҸҷм–‘мқём—җм„ң мң м „м Ғ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„ м җмҲҳлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ м ң 2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқмқҳ мң м „мһҗнҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҳ м—°кҙҖм„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ м—°кө¬н•ң мІ« л…јл¬ёмқҙлқјлҠ” мқҳлҜёк°Җ мһҲлӢӨ. кІ°кіјм ҒмңјлЎң м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ мң м „мһҗнҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҙ кё°мЎҙм—җ м•Ңл Ө진 м—°кө¬л“Өкіј мқјм№ҳн•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң лӮҳнғҖлӮ¬лӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң мІ« 진лӢЁ мӢңм—җ мӮ¬нҡҢм Ғмқ‘ мІӯл Ҙмқ„ к°Җм§Җкі мһҲлӢӨл©ҙ мң м „мһҗнҳ•кіј мғҒкҙҖм—Ҷмқҙ мІӯл Ҙмқ„ мң м§Җн• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ.
ліё м—°кө¬мқҳ м ңн•ңм җмңјлЎңлҠ” лӢЁмқј кё°кҙҖ м—°кө¬мқҙкі , нҷҳмһҗ мҲҳк°Җ л§Өмҡ° м Ғм—Ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ, н•ңкөӯ м ң2нҳ• мӢ кІҪ섬мң мў…мҰқ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мң м „мһҗ нҳ•кіј н‘ңнҳ„нҳ•мқҳ кҙҖкі„м—җ лҢҖн•ң кІ°лЎ мқ„ лҸ„м¶ңн•ҳлҠ” лҚ° н•ңкі„к°Җ мһҲм—ҲлӢӨ. м•һмңјлЎң лӢӨкё°кҙҖ м—°кө¬ л“ұмқ„ нҶөн•ҙ лҚ” л§ҺмқҖ нҷҳмһҗ мһҗлЈҢлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ мқёмў…к°„мқҳ м°ЁмқҙлӮҳ нӣ„м„ұм Ғ мҡ”мқёл“Өмқ„ н•Ёк»ҳ 분м„қн•ҳлҠ” 추к°Җ м—°кө¬к°Җ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң ліҙмқёлӢӨ.
NotesAuthor Contribution Conceptualization: Jong Dae Lee. Data curation: Hyun Tag Kang, Jae Yong Lee, Yun Ji Lee, Se A Lee, Byung Ryul Jeon. Formal analysis: Se A Lee, Jong Dae Lee. Investigation: Hyun Tag Kang. Methodology: Byung Ryul Jeon, Jong Dae Lee. Project administration: Jong Dae Lee. Resources: Jong Dae Lee. Supervision: Jong Dae Lee. Visualization: Hyun Tag Kang, Yun Ji Lee. WritingвҖ”original draft: Hyun Tag Kang, Jae Yong Lee, Yun Ji Lee. WritingвҖ”review & editing: Hyun Tag Kang, Se A Lee, Jong Dae Lee. Fig.В 2.24-year-old male with chief complaint of diplopia. Initial pure tone audiometry shows group D in right ear, and group B in left ear according to American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery classification (A). Gadolinum-enhanced T1-weighted MRI shows huge bilateral involving internal acoustic canal schwannomas involving cerebellopontine angle (right 3.84Г—2.50 cm, left 3.95Г—2.65 cm) (arrows) (B). Cervical-thoracic-lumbar spine MRI shows multiple intradural extramedullary tumor. The patientвҖҷs mutation analysis was negative indicating mild type neurofibromatosis type 2 (arrows) (C). After 1 year follow-up; pure tone audiometry showed worsened hearing level, right ear nearly deaf (D). In Gadolinum-enhanced T1-weighted MRI, the right schwannoma showed a 22% increase in size and the left schwannoma showed 4% increase in size (arrows) (E). 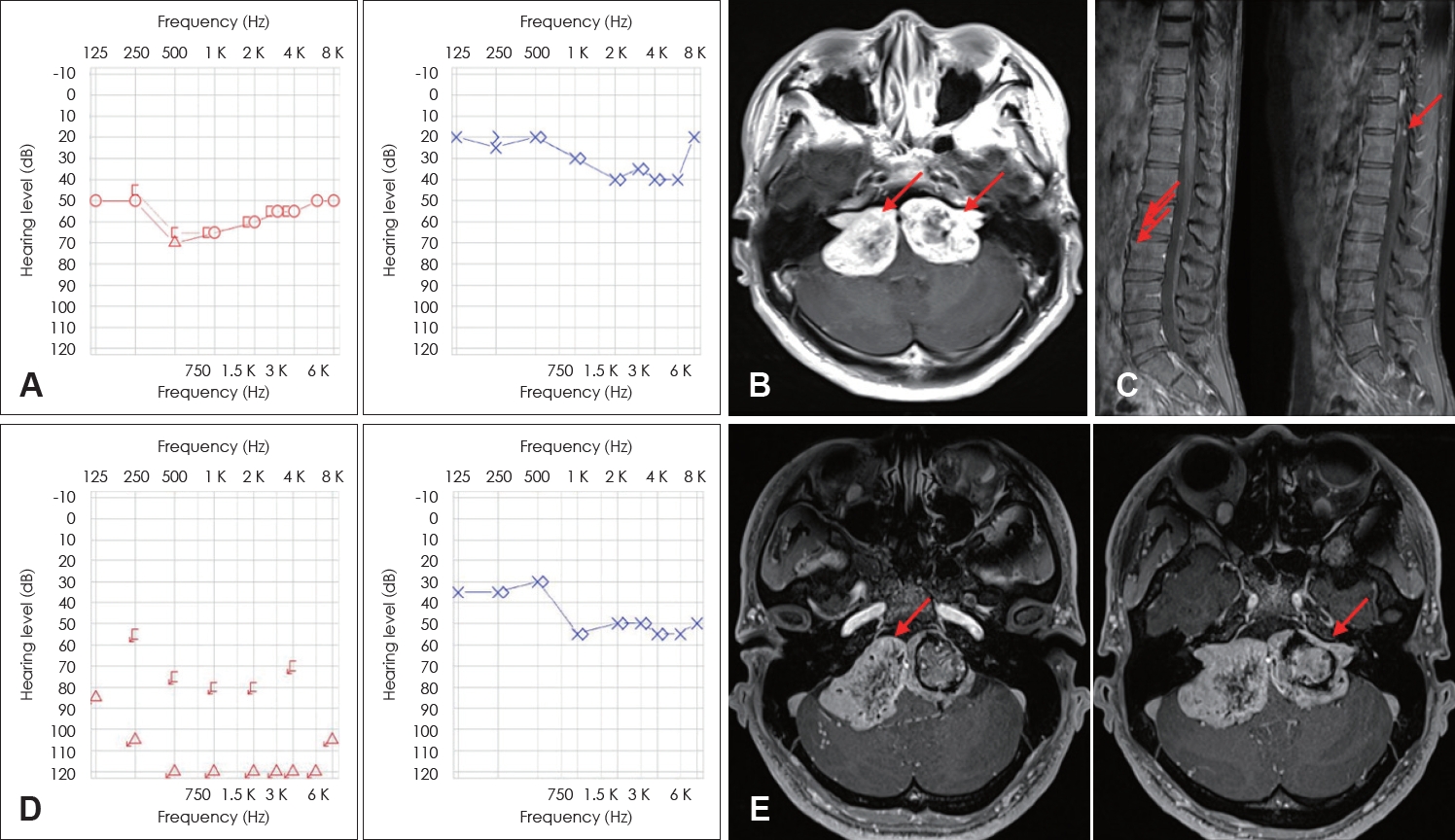
Fig.В 3.20-year-old man with chief complaint of tinnitus. Pure tone audiometry shows normal hearing level on initial visit (A). Gadolinum-enhanced T1-weighted MRI demonstrating bilateral schwannomas involving internal acoustic canal (arrows) (B). Cervical-thoracic-lumbar spine MRI shows multiple intradural extramedullary spine tumor. The patientвҖҷs mutation analysis revealed truncating mutation in exon 11 (c.1119_1120del) indicating severe type neurofibromatosis type 2 (arrows) (C). After 2 years follow-up; pure tone audiometry shows maintained normal hearing level (D). In gadolinum-enhanced T1-weighted MRI, bilateral schwannomas did not show significant size increase (arrows) (E). 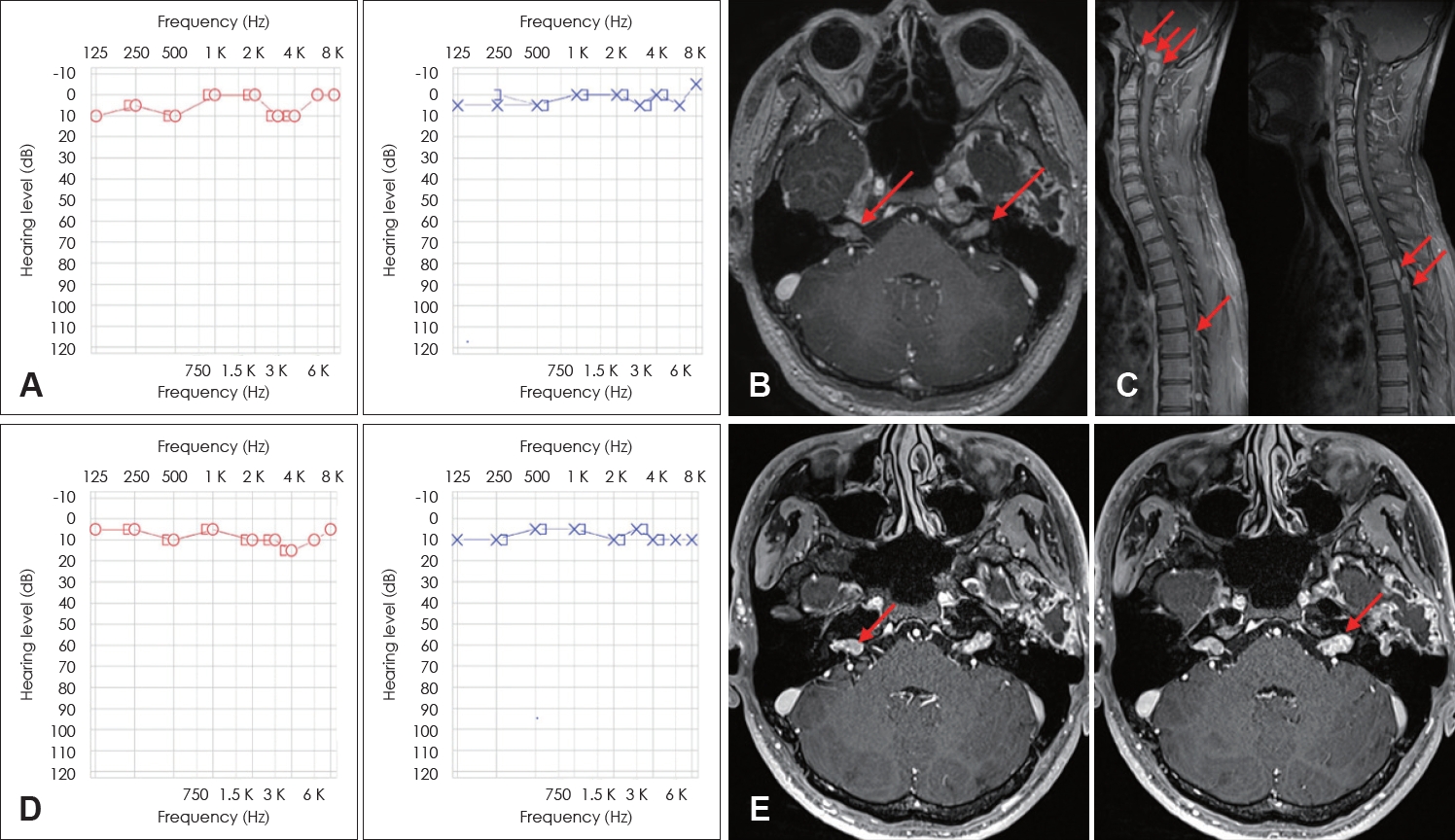
TableВ 1.NF2 clinical diagnostic criteria NF2: neurofibromatosis type 2, VS: vestibular schwannomas. Adapted from Ardern-Holmes, et al. J Child Neurol 2017:32(1):9-22 [3]. TableВ 2.UK NF2 Genetic Severity Score NF2: neurofibromatosis type 2. Adapted from Halliday, et al. J Med Genet 2017;54(10):657-64 [4]. TableВ 3.Demographics of patients with NF2 TableВ 4.Clinical manifestations according to genetic severity grade REFERENCES1. Evans DG. Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): A clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2009;4:16.
2. Asthagiri AR, Parry DM, Butman JA, Kim HJ, Tsilou ET, Zhuang Z, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 2. Lancet 2009;373(9679):1974-86.
4. Halliday D, Emmanouil B, Pretorius P, MacKeith S, Painter S, Tomkins H, et al. Genetic Severity Score predicts clinical phenotype in NF2. J Med Genet 2017;54(10):657-64.
5. Aboukais R, Baroncini M, Zairi F, Bonne NX, Schapira S, Vincent C, et al. Prognostic value and management of spinal tumors in neurofibromatosis type 2 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2013;155(5):771-7.
6. Baser ME, Kuramoto L, Joe H, Friedman JM, Wallace AJ, Gillespie JE, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations for nervous system tumors in neurofibromatosis 2: A population-based study. Am J Hum Genet 2004;75(2):231-9.
7. Kluwe L, Mautner VF. Mosaicism in sporadic neurofibromatosis 2 patients. Hum Mol Genet 1998;7(13):2051-5.
8. Feucht M, Kluwe L, Mautner VF, Richard G. Correlation of nonsense and frameshift mutations with severity of retinal abnormalities in neurofibromatosis 2. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126(10):1376-80.
9. Welling DB, Guida M, Goll F, Pearl DK, Glasscock ME, Pappas DG, et al. Mutational spectrum in the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene in sporadic and familial schwannomas. Hum Genet 1996;98(2):189-93.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 |
 |