정상 면역 환자의 인두후두개 주름에 발생한 원발성 효모균증 1예
A Case of Primary Cryptococcosis of the Pharyngo-epiglottic Fold in an Immunocompetent Patient
Article information
Trans Abstract
Cryptococcus is a pathogenic fungus that can cause various infections mainly in an immunocompromised host. Cryptococcal yeasts are easily inhaled, so pulmonary infection is the most commonly encountered, but in immunocompetent status, primary cryptococcosis occurs rarely in the pharyngo-epiglottic fold. A 75-year-old male came to our clinic with the complaint of foreign body sensation in the throat that lasted for three months. Rigid laryngoscopy showed a circular mass in the pharyngo-epiglottic fold and we performed laryngeal microsurgery with CO2 laser to remove it. The patient was pathologically diagnosed as cryptococcosis. We report this case of rare, atypical cryptococcosis in the pharyngo-epiglottic fold along with a related literature review.
서 론
효모균증(cryptococcosis)은 Cryptococcus neoformans 라는 2-7 μm 크기의 피막화된 효모 양(yeast-like) 진균에 의한 기회 감염이다[1]. 주로 호흡기를 통해 폐에 감염을 일으키며, 면역력이 저하된 경우 및 경구강 국소 스테로이드 사용 시에 잘 발생할 수 있으며, 인후두에 국한되어 발생하는 경우는 비교적 드물다[2,3]. 저자들의 검색에서는 정상 면역기능 환자에서 원발성 인후두 효모균증이 발생한 경우는 영문 검색에서 드물게 있으나, 국내 보고는 없는 것으로 사료된다[2-4].
75세 남자가 3개월 전부터 시작된 경부 이물감을 주소로 내원하였다. 후두 내시경에서 인두-후두개 주름에 원형 종물이 관찰되어, 레이저 후두미세수술로 효모균증으로 최종 진단 되었다. 저자들은 정상 면역력의 성인에서 발생한 드문 원발성 인후두 효모균증을 경험하여 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고한다.
증 례
75세 남자가 3개월 전부터 시작된 인후두 이물감을 주소로 내원하였다. 헛기침을 반복적으로 하였으며, 음성 변화, 객담, 기침, 연하곤란 및 위산 역류 등은 저명하게 호소하지 않았다. 1차 병원에서 시행한 3개월 동안의 수소이온차단제 투약에 뚜렷한 증상 호전은 없었다. 당뇨, 고혈압, 고지혈증 및 갑상선기능저하증 등이 있었고, 경구 및 국소 경구강 스테로이드 사용과 항암제 투약 등의 병력은 없었다. 흡연력은 30갑년이지만, 10년 전부터 금연하였으며, 음주력은 미미하였다. 경성 후두내시경에서 우측 인두-후두개주름에 표면이 매끈한 양상의 원형 종물이 관찰되었다(Fig. 1A and B). 성대진동검사에서 점막 파동은 정상 소견이었고, 청지각적 음성검사에서는 모두 정상 범위였다. 컴퓨터단층촬영에서 우측 인후두개 주름에서 기시하는 약 8×9 mm 크기의 조영증강되는 외장성 원형 종물이 관찰되었으며, 비정상적인 림프절비대를 포함한 다른 특이소견은 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 2). 굴곡형 내시경을 통한 생검에서는 소수의 림프구만 관찰된다고 보고되었다.
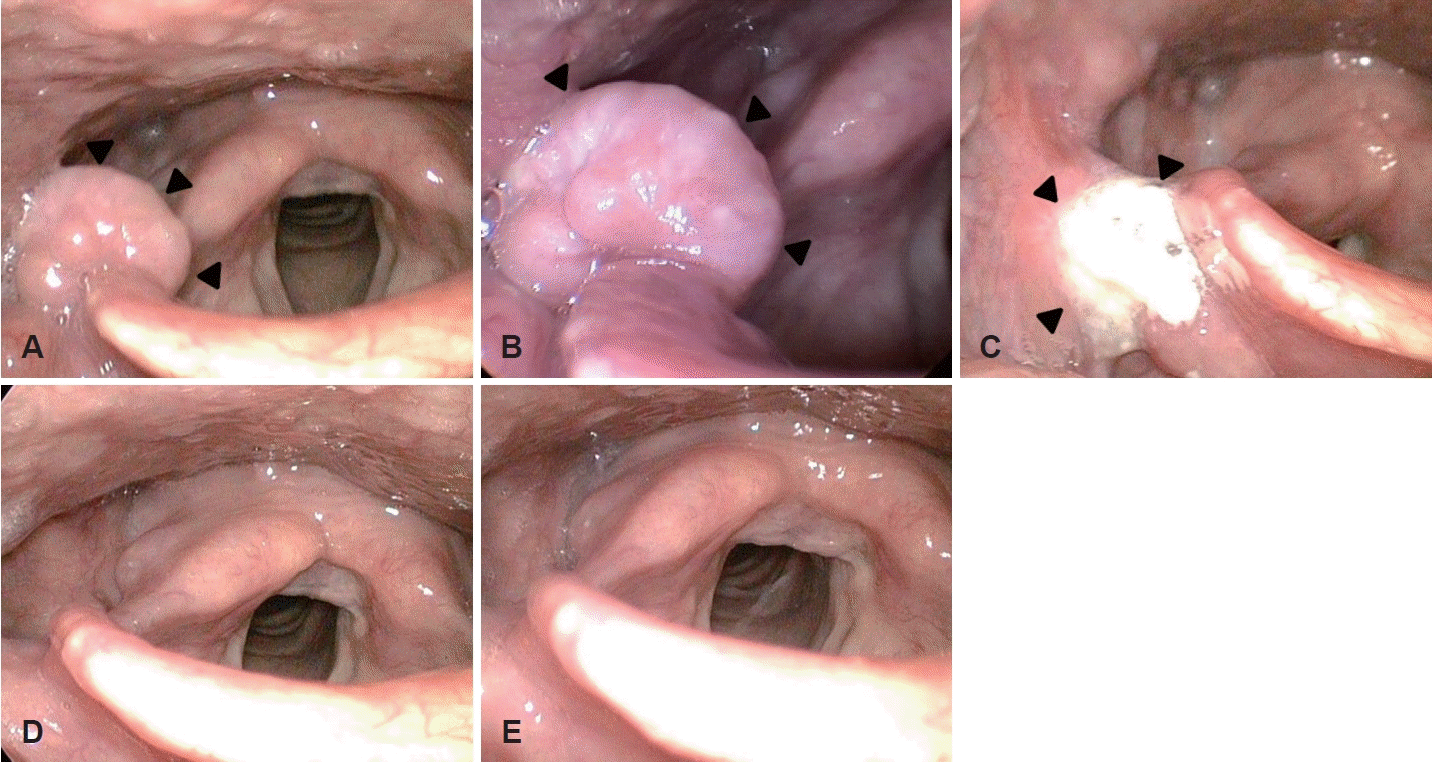
The rigid laryngoscopic findings. A and B: It shows a circular, exophytic mass in the right pharyngo-epiglottic fold (arrowheads). C: At the postoperative one month, it appears to be a normal wound healing process (arrowheads). D: Three months later, it shows well healed lesion and no evidence of relapse. E: It shows similar findings at the post-operative six months.
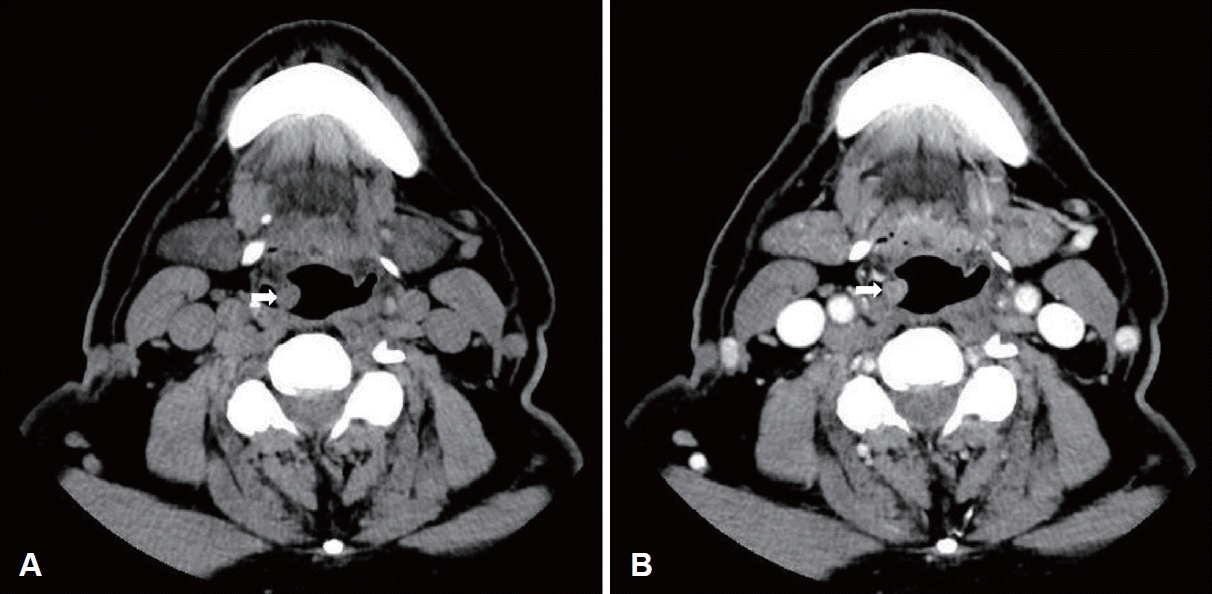
The radiologic findings. A: The non-enhanced axial neck CT scan shows about 8×9 mm sized exophytic mass in the right lateral pharyngo-epiglottic fold (arrow). B: The enhanced image shows slight enhanced pattern in the same site (arrow).
내시경 및 영상 소견 등에서 종물의 양상이 특이하고, 자연 소실 가능성이 적어 보이고, 환자도 수술적 제거를 원하여, CO2 레이저를 이용한 후두미세수술을 계획하였다. 현수 후두경을 위치시키고, 인두-후두개 주름과 종물 사이에 출혈 방지를 위해서 혈관결찰 클립 2개를 먼저 거치하고, 지속 슈퍼펄스 방법으로 2.5와트 강도의 CO2 레이저(AcuPulseTM; Lumenis Ltd., Yokneam, Israel)를 사용하여 원형 종물을 절제하였다(Fig. 3A and B). 종물은 주변 조직과 유착이 있었으며, 절제 시 중등도의 출혈이 발생하였다. 조직병리 검사에서는 종물의 절단면 육안소견은 원형 회백색의 연조직 양상이었다(Fig. 4A). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) 염색에서 육아종성 염증소견 내 둥근 타원형의 피막에 둘러싸인 효모 구조를 관찰 할 수 있었고, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)와 Grocott methenamine silver (GMS) 염색 등을 통한 효모균 다당류 캡슐의 양성 소견, Fontana-Masson (FM) 염색에서 다핵거대세포의 세포질에 존재하는 양성 유기물을 확인하여, 효모균증으로 최종 진단되었다(Fig. 4B-E). 진균 배양 검사는 시행하지 않았으며, 다른 진균 감염을 배제하기 위해 캔디다 및 아스페르길루스 등에서 상승되는 혈청(1-3)-beta-Dglucan은 음성이었으며, 혈청 효모균 항원 역가(cryptococcus antigen titer)는 1:8 (참고값 <1:4)로 경미한 상승을 보였다. 병리 결과 보고 후, 시행한 저선량 흉부 CT와 면역력 이상 여부를 확인하기 위해 시행한 면역글로불린, 보체 및 NK 세포 활성도 평가를 위한 인터페론 감마 등의 혈청 검사에서 모두 정상범위로 보고되었다. 이상의 소견으로 일차성 인후두 효모균증으로 진단하고, 감염내과에 의뢰하여 6주 동안 플루코나졸(fluconazole)을 400 mg/1회/일 용량으로 투약하였다.

The operative microscopic findings. A: It shows well margined round mass. B: After removal of mass with CO2 laser, several surgical clips are observed without bleeding.
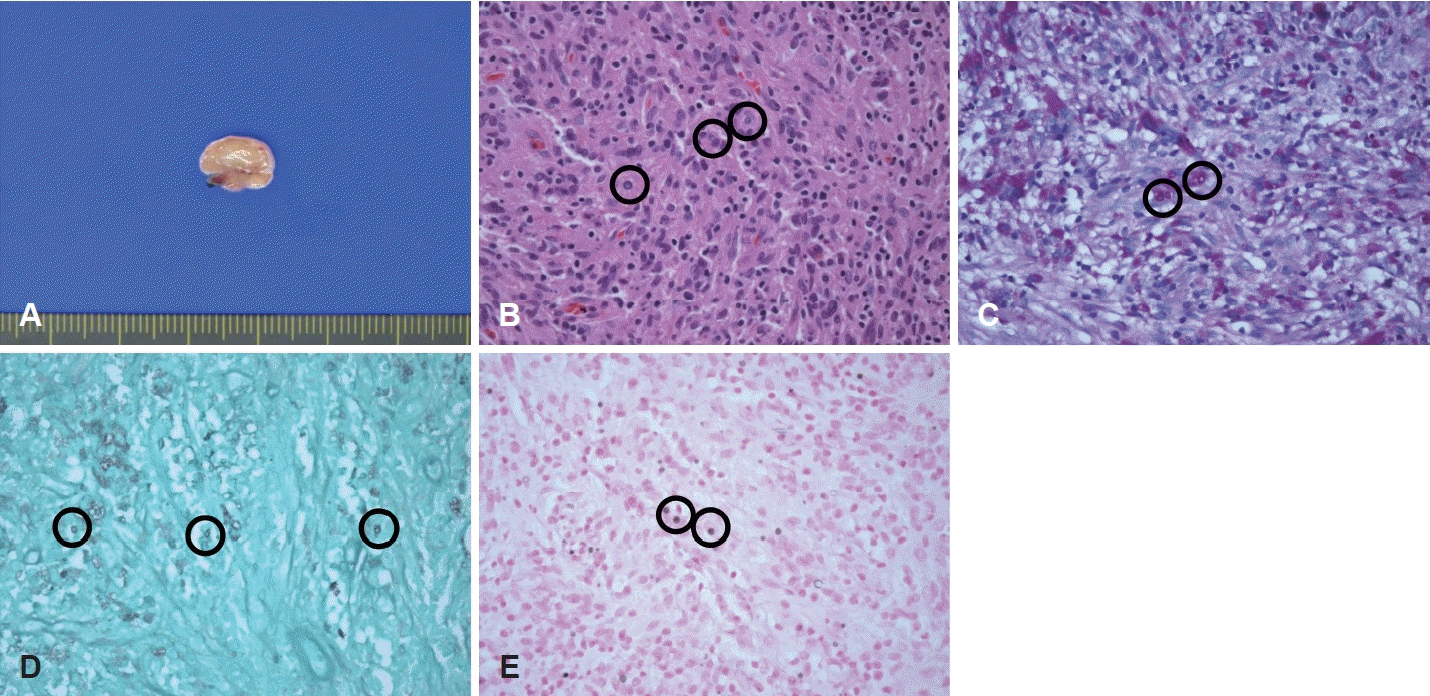
The pathologic findings. A: Gross finding of cut surface of mass is round whitish yellow and soft appearanc. B: The histopathologic findings demonstrate encapsulated round to oval yeast structures in granulomatous inflammation (circles) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400). C: Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive prominent capsules of spherules are observed (circles) (PAS stain, ×400). D: Thin cell walls of Cryptococcus are noted by Grocott methenamine silver (GMS) stain (circles) (GMS, ×400). E: Due to melanin production of Cryptococcus, Fontana-Masson (FM) stain was positive (circles) (FM, ×400).
술후 2일에 부종 및 출혈 등의 소견 없이 퇴원하였고, 술후 4주에 시행한 후두 내시경 검사에서 수술 부위 점막의 정상 치유 과정이 관찰되었으며, 술후 2주 후부터는 서서히 이물감도 호전되고, 3개월 후에는 경미한 정도만 호소하였다. 술 후 3개월과 6개월에 각각 시행한 후두내시경 검사에서 재발 소견은 없었으며(Fig. 1C-E), 8개월이 경과한 현재까지 재발 없이 추적 관찰 중이다.
고 찰
효모균증은 효모균(Cryptococcus)에 의한 침습성 진균 감염으로 Cryptococcus neoformans와 Cryptococcus gatti 등이 흔하다[4,5]. 조류의 배설물에 서식하여 공기 중에 떠돌아 쉽게 흡인될 수 있고, 가장 흔한 감염 부위는 폐로 알려져 있다[1]. 그 외 중추신경계, 피부, 전립선, 눈, 골, 요로, 혈액 등에 발생할 수 있으며[1,6], 후두의 경우는 진성대 및 가성대 등에 호발한다[1]. 상기도의 후두 효모균증은 스테로이드제제, 면역억제제 등의 사용 또는 후천성 면역결핍증 환자에서 잘 발생하지만, 정상 면역을 가진 사람에게서도 드물게 발생할 수 있다[4,7].
진단에는 후두내시경과 조직검사 등이 유용하다[2]. 내시경 소견은 부종, 외장성 종물형, 홍반 및 백색반 등의 다양한 양상으로 관찰될 수 있으며, 본 증례와 같이 표면이 매끈한 원형 종물로 보일 수도 있다[2]. 조직학적으로 진균을 구분하기 위해서는 H&E 염색, GMS, PAS 및 alcian blue 등과 같은 여러 염색법이 필요하다[7]. 혈청 효모균 항원 역가는 진단에는 보조적 소견이나, 치료 과정에서 역가 수치 하락 추세 및 음성화 등을 통해 치료 반응 평가에 유용하게 사용된다[2].
전형적인 영상 소견은 없으며, 병변의 형태에 따라서 다양 게 보일 수 있으며, 일반적으로 조영 증강 되며, 악성 병변과 유사한 양상으로 보일 수도 있다[1]. 내시경 소견으로만 효모균증을 진단하기는 어렵고, 감별 진단을 위해 조직학적 검사가 필수적이다[1]. 본 증례는 조직병리 소견과 혈청 항원 역가 상승 소견 등으로 배양 검사 없이 효모균증으로 확진하였다. 본 진균증의 확진에 배양 검사가 반드시 필수적인 것은 아니고, 위 두 가지 소견으로 진단의 민감도가 93%-100%, 특이도는 93%-98% 등으로 효모균증의 확진에 무리가 없다는 보고가 있다[8,9].
치료는 면역 저하 유무 및 뇌수막염 등과 같은 중추신경계의 침범 여부에 따라 결정되며, 중추신경계 침범을 동반하지 않은 정상 면역 환자의 경우 6-12개월 동안 플루코나졸을 하루 4 00 mg의 용량으로 복용이 권고되나, 아직 근거 기반의 명확한 치료 지침은 정립되지 않았다[6,10]. 그러나 초기 항진균제 약물 치료에 불응하거나 병변이 크고, 외장성 종물인 경우 선택적으로 레이저 후두미세수술을 통한 병변의 제거가 치료에 도움된다는 보고가 있다[2]. 본 증례는 이물감이 저명하고, 악성 및 육아종성 병변 등과의 감별을 위해 후두미세수술을 시행하였고, 감염내과의 권고에 따라서 항진균제 치료를 시행하였다.
문헌 검색으로는 원발성 인후두 효모균증은 영문검색에서 드물게 보고되어 있지만[1-4] 국내 보고는 없으며, 정상 면역 상태에서의 발생은 더욱 드물다. 저자들은 본 증례를 경험하면서 면역력 결핍이 없거나, 장기간의 스테로이드 사용이 없는 경우에도 인후두 종물의 감별진단에 드물지만 효모균증의 가능성도 염두에 두면서 진단 및 치료 등에 임해야 한다는 교훈을 얻었다.
Acknowledgements
None
Notes
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: Seung Woo Kim. Data curation: Hyeok Ro Kwon, So Young Ko. Formal analysis: Hyeok Ro Kwon, So Young Ko. Investigation: So Young Ko. Methodology: Hyeok Ro Kwon, Mi Ji Lee. Supervision: Seung Woo Kim, Mi Ji Lee. Validation: Seung Woo Kim. Visualization: Mi Ji Lee. Writing—original draft: Hyeok Ro Kwon. Writing—review & editing: Seung Woo Kim.
