Introduction
Thyroid nodules are a common finding in head and neck clinics [1,2]. The prevalence of thyroid nodules is 49%-67% on ultrasonography (US), and it increases with age, with 59.4% in the 60s, 65.5% in the 70s, and 73.7% in the 80s and older [2,3]. Although most thyroid nodules are benign and asymptomatic, a small proportion (10%-15%) may increase in size over time, causing symptoms or cosmetic problems, which are treated using simple aspiration or surgical excision [1]. However, simple aspiration for thyroid cysts is not considered a curative treatment due to a high recurrence rate. Concurrently, surgery may be associated with various complications, such as bleeding, vocal cord paralysis, hypothyroidism, and cosmetic deformity caused by the surgical scar [1].
Therefore, non-surgical and minimally invasive treatments, including ethanol ablation (EA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA), have been introduced and have gained popularity for their safety and effectiveness in managing benign thyroid nodules [1,4]. Accordingly, several international societies or study groups have published guidelines or consensus statements regarding EA and RFA as primary treatments for benign thyroid nodules [1,4]. These techniques involve various complications, including pain, voice change, and hematoma, which are manageable with conservative treatment in most cases.1) Infection is rare because the thyroid gland is resistant to infection due to its abundant blood supply, high iodine content, and good lymphatic drainage [5]. Moreover, thyroid abscess following EA requiring surgical intervention is extremely rare and has been reported only once [6].
Herein, we report a case of thyroid abscess following EA for a benign thyroid nodule that required surgical treatment, raising awareness of a life-threatening complication and introducing possible pathogenesis for this phenomenon.
Case
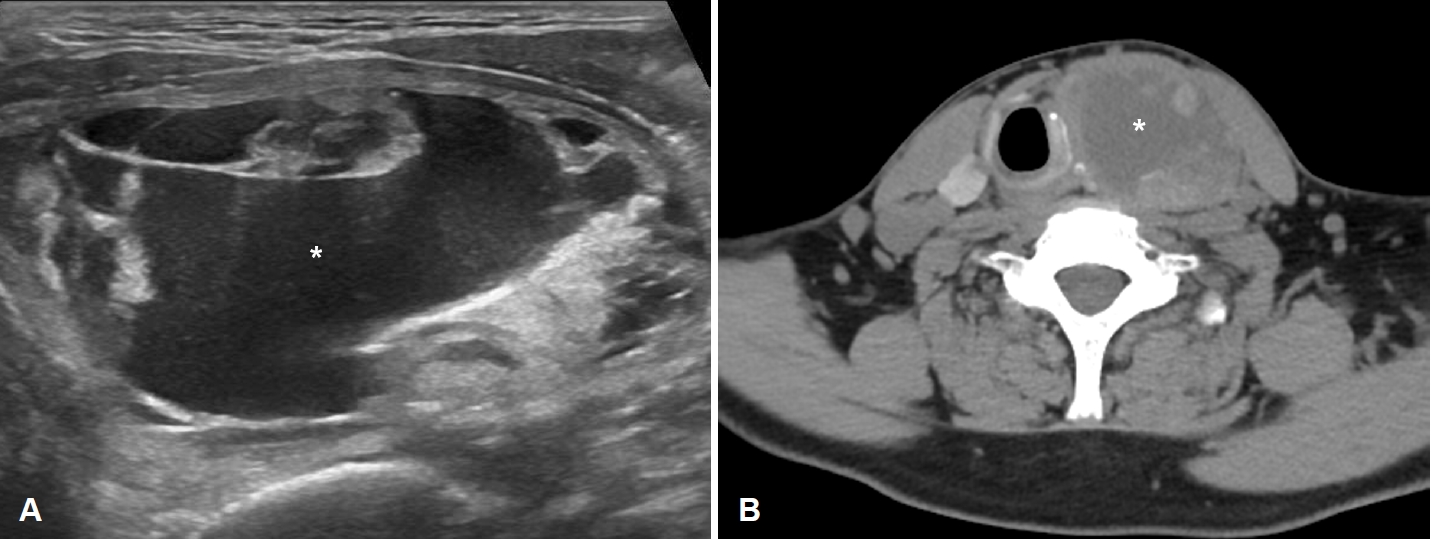
A 46-year-old male visited our emergency room complaining of severe, painful anterior neck swelling that caused dyspnea and dysphagia. He had underlying hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and cerebral infarction. The patient had a history of a large thyroid nodule that had developed approximately one year ago. The nodule was predominantly cystic and 5.4Г— 4.4Г—7.1 cm in size as detected using US and CT (Fig. 1A and B). To diagnose the left thyroid nodule, he underwent three rounds of US-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy. All the biopsy results were benign and consistent with nodular hyperplasia. Considering the nodule size, cosmetic deformity caused by the nodule, and the patientвҖҷs underlying disease, US-guided EA was recommended, and two sessions of USEA were performed. During the first EA session, 23 mL of cyst fluid was aspirated, and 10 mL of ethanol was injected into the nodule. After the first EA, the nodule was observed to remain stationary with decreased cystic portion. However, at the 6-month follow-up, it was found to have increased in size to 6.9Г—3.6Г—7.4 cm. On US examination, significant internal debris was also observed, which could be attributed to the initial EA (Fig. 2). As a result, a second session of EA was performed, during which 18 mL of cyst fluid was aspirated, and 6 mL of ethanol was injected into the nodule. On the day after the second EA session, painful swelling of the left anterior neck developed, causing dyspnea and dysphagia. The initial vital signs, including blood pressure, body temperature, and respiratory rate, were within the normal range in the emergency room. The saturation of peripheral oxygen was 97% despite the patientвҖҷs complaint of dyspnea. Physical examination revealed severe swelling in the left thyroid lobe, and no other palpable masses were observed. Laboratory tests revealed white blood cell (WBC) counts of 14530/ВөL (reference range, 4800-10800/ВөL), C-reactive protein level of 39.59 mg/dL (reference range, <0.50 mg/dL), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 120 mm/h (reference range, 0-10 mm/h).
US showed a large, heterogeneous hypoechoic lesion with multiple hyperechoic foci and surrounding soft tissue edema in the left thyroid gland (Fig. 3). These findings suggested an inflamed mass with necrosis. CT demonstrated a 7.5Г—6Г—10 cm-sized low attenuation mass with necrosis and air foci in the left thyroid lobe displacing the trachea to the right (Fig. 4). These findings were consistent with those of a large thyroid abscess that compromises the upper airway. An emergency incision and drainage were performed. Intraoperative findings revealed severe necrosis of the previously ablated left thyroid nodule with a large amount of pus. Extensive irrigation and additional debridement of necrotic tissue were performed, and the operation was concluded after inserting a drain catheter. Microbiological examination of pus revealed no WBC on the wet smear, no microorganisms on gram staining, and no growth in the pus culture. A biopsy performed on the left thyroid gland, which was removed intraoperatively, revealed benign lesions. The patient received 2-weeks of medical treatment, including empirical antibiotics and steroids, and was discharged without complications.
Discussion
This case shows that EA for treating benign thyroid nodules could be associated with life-threatening complications compromising the airway. To the best of our knowledge, this is the second case report of a thyroid abscess following EA for a benign thyroid nodule that required surgical intervention. The first case of thyroid abscess after EA was reported in 2021, which introduced the development of a thyroid abscess one week after EA in a 63-year-old male with type 2 diabetes [6]. The patient was ultimately treated with subtotal thyroidectomy due to persistent abscess even after a large amount of pus aspiration and sufficient medical treatment based on microbiological culture results (positive for Staphylococcus aureus) [6]. Unlike the previous report, in our case, signs and symptoms of thyroid abscess developed the day after the second EA. Moreover, all microbiological examinations of the pus revealed negative results on the wet smear, Gram stain, and pus culture, which was an exceptional finding when compared to cases of abscess as a result of infection. Based on these findings, we suggest that a thyroid abscess resulting from chemical necrosis caused by injected ethanol should be considered primarily rather than a thyroid abscess resulting from bacterial infection. The therapeutic mechanism of EA is a combination of coagulative necrosis due to cell dehydration and ischemic necrosis by thrombus formation in the small blood vessel [1]. This tissue reaction following EA can also lead to the release of breakdown products, inflammatory mediators, and vasoactive substances from the necrotic tissue [7,8]. Although such complication has not been reported after EA for a thyroid nodule, a similar phenomenon has been well recognized in cases of hepatic abscess after chemical embolization for malignant hepatic tumors [9]. In the hepatic abscess after chemical embolization, the primary mechanism is the ischemic destruction of the intrahepatic ducts rather than a bacterial infection [9]. Additionally, post-embolization syndrome, characterized by the development of pain, fever, and nausea within the first 72 hours after embolization of a solid organ, is also caused by degradation products and inflammatory mediators released by tissue hypoxia and cell death [7]. Moreover, considering the strong bactericidal potential of 99% ethanol, it is challenging to presume that an immediate bacterial infection after EA primarily contributed to the development of thyroid abscess [10]. Therefore, thyroid abscess induced by chemical necrosis is a transpirable pathogenesis that can occur after EA for benign thyroid nodules. However, the possibility of bacterial infection accompanying this chemical necrosis cannot be completely excluded, as this type of complication is rare, and its exact pathogenesis is difficult to determine in clinical practice. Additionally, the patientвҖҷs underlying diseases, particularly chronic kidney disease, could contribute to the accelerated progression of tissue necrosis caused by chemical damage. This is due to the accumulation of uremic toxins and chronic inflammation caused by chronic kidney disease, which impairs wound healing [11].
Chung, et al. [12] reported nodular rupture in 12 patients over 8 years after RFA as a serious complication after non-surgical treatment for benign thyroid nodules requiring surgical intervention. In their study, the primary symptoms and signs (painful neck swelling) occurred 54 days after RFA on average, and surgical treatment was performed in 2 of 12 cases. Based on CT findings of high attenuation and the hemorrhagic nature of the aspirated fluid, hematoma resulting from delayed bleeding after RFA was presumed to be the primary mechanism of nodular rupture, as opposed to our case. In contrast to RFA, which can be used for both cystic and solid thyroid nodules, EA is typically reserved for benign cystic nodules, which account for only 15%-20% of all thyroid nodules [13]. As a result, there may be relatively fewer reports of major complications after EA as compared to that after RFA. Despite this, over 100 studies have been conducted on EA for thyroid nodules, which is sufficient to include the majority of major/minor complications associated with the procedure. This highlights the rarity of the present case [1,14].
Early diagnosis is important when a thyroid abscess is suspected to be a cause because the disease may progress rapidly and be life-threatening. CT and US are the most valuable imaging modalities for diagnosing thyroid abscesses. Although definitive guidelines are not yet available because of their low prevalence, immediate administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics is empirically used [15]. Blood and pus culture from aspiration or tissue sampling are also mandatory for appropriate antibiotic selection [15]. Thyroid abscess with airway compromise requires immediate surgical drainage. A persistent thyroid abscess or clinical exacerbation despite adequate antibiotic administration following surgical drainage requires thyroidectomy, and resection of the thyroid tissue is needed in cases with extensive necrosis [5].
In conclusion, this case showed that EA could lead to a thyroid abscess, possibly mediated by chemical necrosis and subsequent inflammatory reactions. Although this complication is infrequent, it may become more prevalent as the use of EA rapidly increases. Head and neck surgeons should remain alert and recognize the risk of a thyroid abscess as a complication of EA.